The term “mining” is inseparable from discussions about cryptocurrency.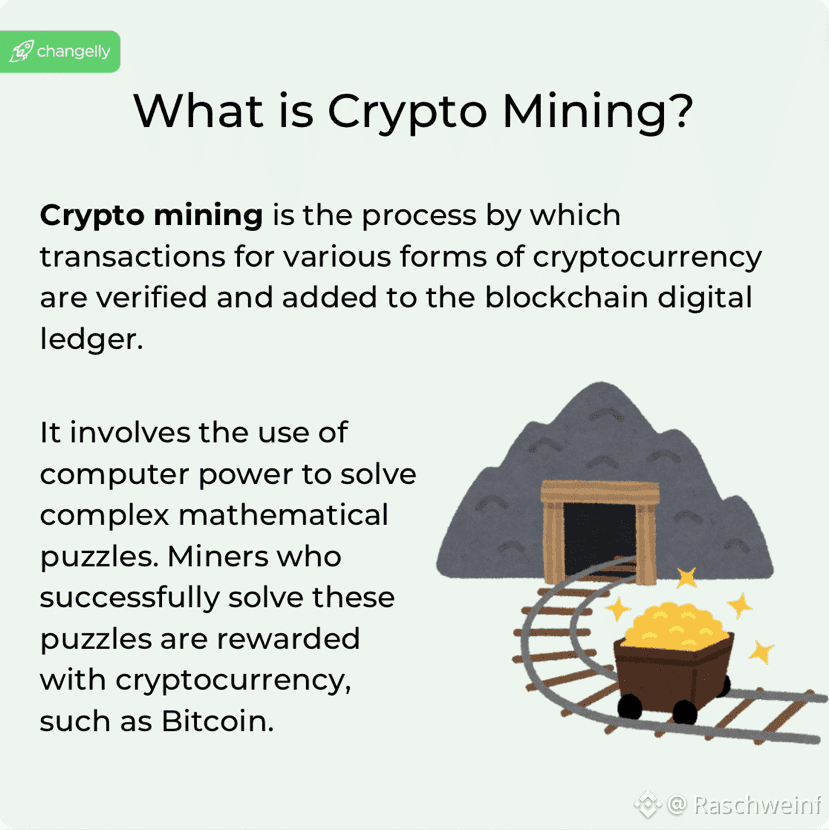
Mining is the process of verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain network (Dirgantara, 2023). This process also generates new bitcoins, which are then released into circulation. Mining is performed by solving complex mathematical puzzles. It is called “mining” because, through the validation of transactions and the addition of new blocks to the blockchain, new bitcoins are created—similar to how mining gold requires effort and resources.
Likewise, Bitcoin mining requires significant computational power. To validate Bitcoin transactions, miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles using specialized computers known as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs). The mining process is governed by a mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW), which regulates how new transaction blocks are added to the blockchain.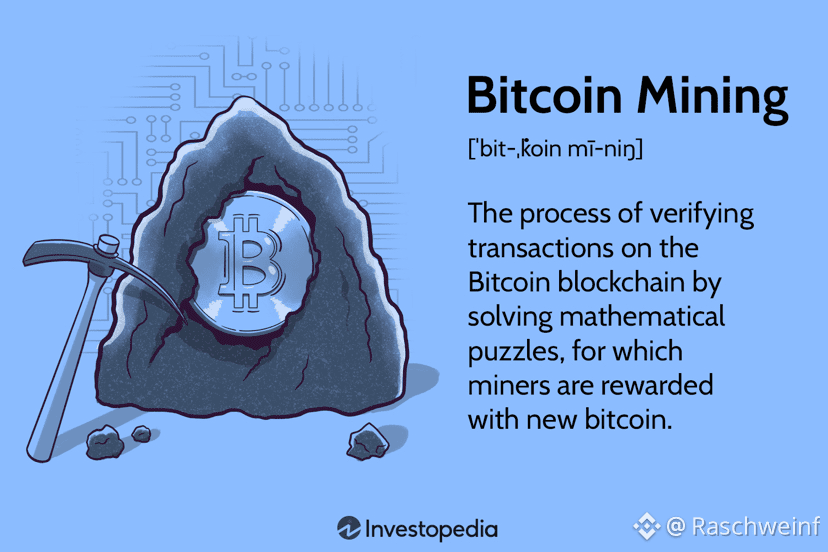
Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered, because any change would modify the hash of that block and all subsequent blocks. A hash itself is a cryptographic output consisting of 64 hexadecimal characters, which makes the system highly secure and extremely difficult to tamper with.
Between 2020 and 2024, miners who successfully mined Bitcoin received a reward of 6.25 BTC per block. This reward is reduced approximately every four years in order to maintain Bitcoin’s scarcity and long-term value. This reduction process is known as the Bitcoin Halving.