Most public blockchains were designed around radical transparency. While this openness supports auditability and trustless verification, it becomes a structural limitation when smart contracts are used for real-world financial and institutional applications.
This is where confidential smart contracts change the equation.
Instead of exposing every transaction detail on a public ledger, confidential smart contracts selectively protect sensitive data while preserving verifiability unlocking use cases that standard smart contracts cannot safely support.
The Core Limitation of Public Smart Contracts
In traditional public smart contracts:
Transaction inputs and outputs are fully visible
Contract state changes can be monitored in real time
Business logic is often exposed on-chain
This level of transparency works for simple DeFi primitives, but it breaks down in environments where privacy, compliance, and competitive protection are required.
Institutions cannot operate efficiently if pricing models, identities, or strategies are publicly observable.
Key Advantages of Confidential Smart Contracts
1. Data Privacy Without Sacrificing Verification
Confidential smart contracts are built to shield sensitive information such as transaction amounts, identities, or contract logic from public view. This is achieved using cryptographic techniques or secure execution models, rather than trust-based off-chain processes.
Crucially, data can remain private while still being provable to authorized parties—a requirement for regulated markets.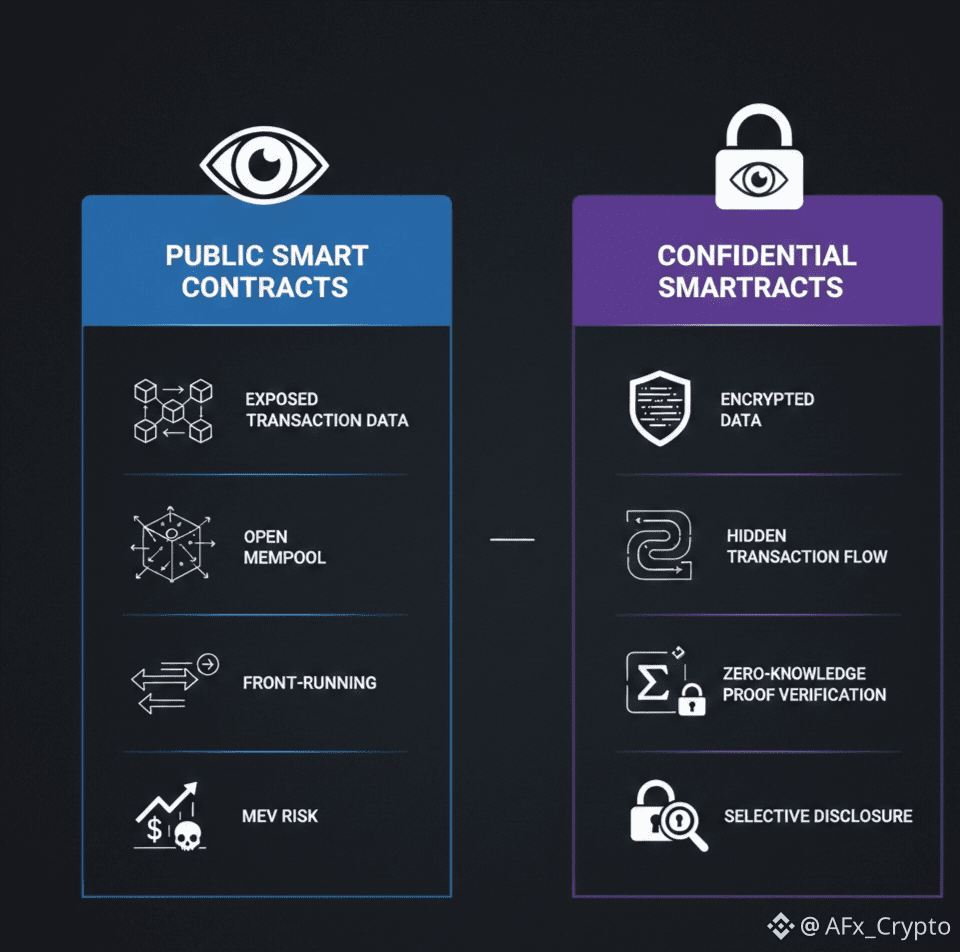
2. Compliance by Design, Not Afterthought
Regulations such as GDPR, financial disclosure rules, and data protection laws require strict handling of personally identifiable information (PII).
Confidential smart contracts allow sensitive data to remain off-ledger while maintaining on-chain settlement and verification. This makes them far more suitable for:
Tokenized securities
Private equity instruments
On-chain financial agreements
Transparency is preserved where needed, and privacy is enforced where required.
3. Reduced Security and Market Risks
Public mempools introduce several well-known risks:
MEV extraction through transaction visibility
Front-running of large or strategic trades
Exposure of proprietary strategies
By encrypting transaction details until execution, confidential smart contracts significantly reduce these attack surfaces. Sensitive logic and positions remain protected, preserving both capital efficiency and competitive advantage.
Expanding Blockchain’s Practical Use Cases
Confidential execution is not just about hiding data—it enables entire categories of applications that public contracts struggle to support:
Financial transactions where pricing and counterparties must remain private
Healthcare data management, where public exposure is unacceptable
Fair auctions and voting, where secrecy is required until settlement
Self-sovereign identity, where users selectively disclose information
Without confidentiality, these use cases either remain off-chain or rely on fragile workarounds.
How Dusk Network Approaches Confidentiality Differently
Dusk Network focuses on privacy-preserving smart contracts designed specifically for regulated environments.
Instead of full anonymity, Dusk implements selective privacy—data remains confidential by default but can be verified by authorized parties when required. This is a critical distinction for compliance-driven applications.
Key to this design is the use of zero-knowledge proofs, which allow confidential computation while maintaining on-chain validity. The result is a system that balances:
Privacy
Regulatory alignment
Verifiability
This makes Dusk particularly suitable for tokenized financial instruments and legally compliant on-chain agreements.
Transparency vs Confidentiality Is a False Trade-Off
Standard smart contracts excel in open, permissionless experimentation. However, as blockchain adoption moves toward institutions and regulated markets, privacy becomes infrastructure, not a feature.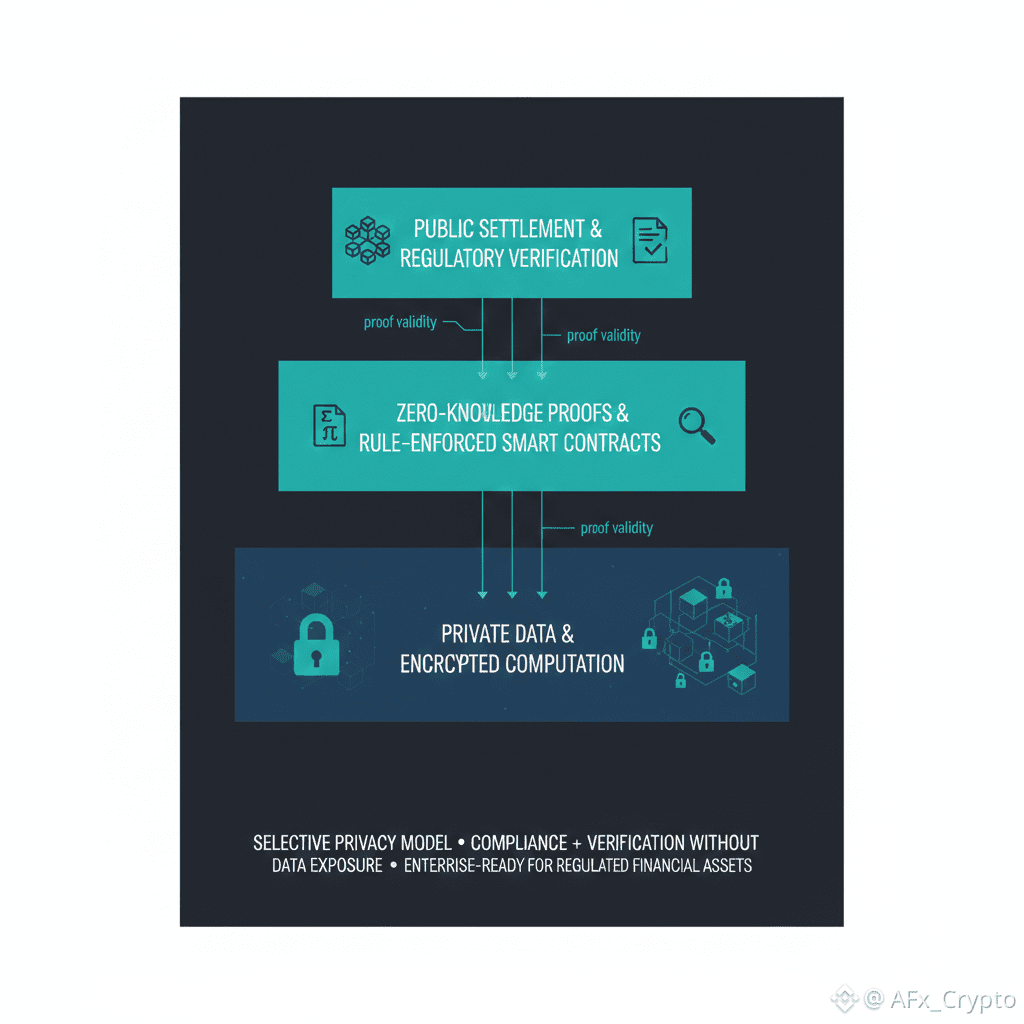
Confidential smart contracts address this gap directly extending blockchain’s reach into sectors where transparency alone is insufficient.
By combining cryptographic privacy with verifiable execution, networks like Dusk demonstrate how blockchain can evolve beyond speculation and into compliant, real-world deployment.

