Most blockchains were created for open participation and radical transparency. While this works for peer-to-peer transfers and retail DeFi, it breaks down the moment regulated finance enters the picture. Financial institutions do not operate in public view, and they cannot rely on systems that ignore legal structure. Dusk Network approaches blockchain from the opposite direction. It starts with the needs of institutions and engineers decentralization around them.
At its core, Dusk is a purpose-built Layer-1 blockchain designed for professional financial markets. The network is not focused on yield farming, memes, or short-term speculation. Its architecture is shaped around long-term financial operations such as asset issuance, trading, custody, and settlement. Every design decision reflects the assumption that real money, real companies, and real regulation will interact on-chain.
One of the most important engineering choices behind Dusk is how it treats identity. Traditional blockchains treat users as anonymous addresses, which is incompatible with regulated finance. Dusk introduces identity primitives that allow participants to prove eligibility without exposing their full identity on-chain. This means an investor can demonstrate compliance with rules such as accreditation or jurisdictional limits while remaining private to the public network. For institutions, this is a necessary step toward adoption.
Dusk also introduces a new way of thinking about smart contracts. On many networks, smart contracts are powerful but blind to legal context. On Dusk, contracts are designed to be regulation-aware. This means the rules governing an asset or financial product are not external agreements but encoded directly into its logic. Transfers, ownership changes, and lifecycle events can all be restricted or permitted automatically based on predefined conditions.
This approach dramatically reduces operational risk. Instead of relying on off-chain checks or manual compliance processes, the blockchain itself enforces the rules. Errors caused by human oversight or mismatched systems become far less likely. For financial institutions, this reliability is often more valuable than raw transaction speed.
Another defining feature of Dusk is how it handles transaction visibility. Not every transaction needs to be private, and not every transaction should be public. Dusk allows different levels of visibility depending on the use case. Public transactions can coexist with confidential ones on the same network. This flexibility allows applications to choose transparency where it makes sense and privacy where it is required.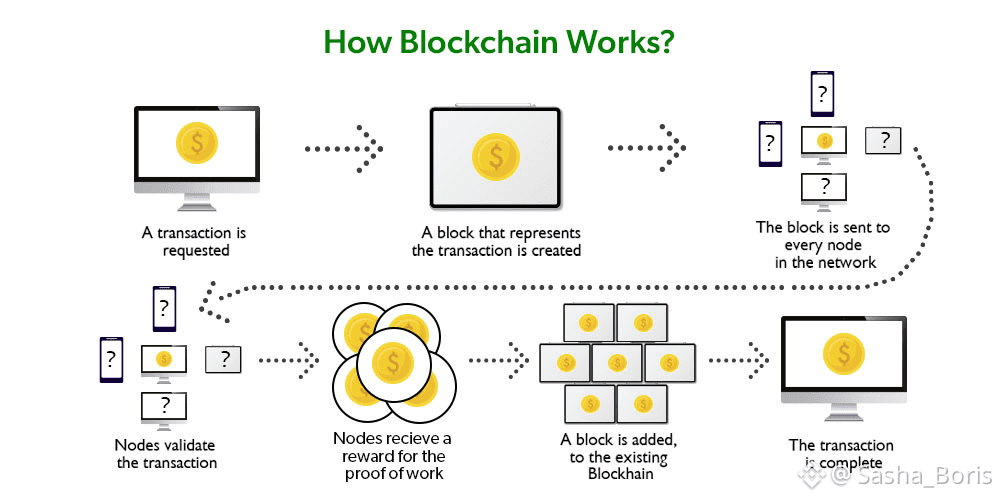
From a technical perspective, Dusk is optimized for predictable outcomes. Financial systems depend on certainty, not probabilistic behavior. The network emphasizes clear finality, meaning once a transaction is confirmed, it is settled beyond dispute. This is especially important for activities like trading, clearing, and settlement, where delays or reversals can have serious financial consequences.
The staking and consensus model of Dusk supports this need for stability. Validators are economically aligned with the long-term health of the network, and incentives are structured to discourage behavior that could compromise reliability. This creates an environment where institutions can trust the underlying infrastructure, rather than treating it as an experimental system.
Dusk’s ecosystem is also designed to integrate with existing financial and technical infrastructure. Rather than isolating itself, the network supports familiar development patterns and tools. This makes it easier for teams with traditional finance or enterprise backgrounds to build on Dusk without retraining from scratch. Over time, this lowers adoption friction and accelerates ecosystem growth.
As the network matures, Dusk is positioning itself as more than just a blockchain. It is evolving into a financial coordination layer where multiple regulated actors can interact securely. Issuers, investors, platforms, and service providers can operate within the same system while maintaining clear boundaries around data access and responsibility.
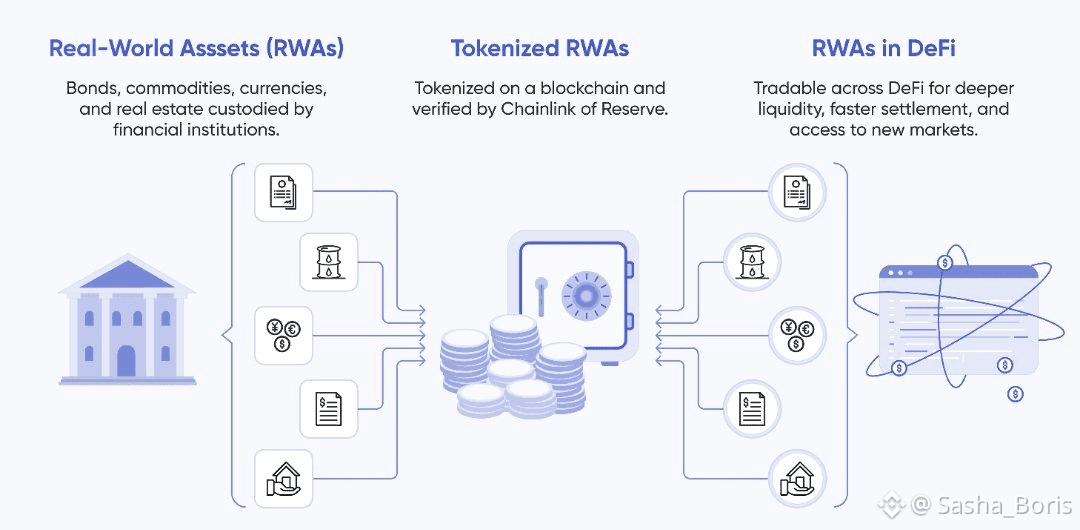
Looking ahead, Dusk’s role becomes increasingly important as global finance moves toward tokenization. Bringing real-world assets on-chain is not just a technical challenge; it is a legal and operational one. Dusk addresses this reality head-on by embedding regulation, privacy, and financial logic into its core design.
Rather than promising to disrupt finance overnight, Dusk takes a more realistic approach. It focuses on building infrastructure that institutions can actually use, regulators can understand, and markets can trust. In doing so, Dusk Network is quietly redefining what decentralized finance can look like when it is built for the real world, not just the open internet.