@Fogo Official Blockchain infrastructure has evolved rapidly over the past decade, but many networks still struggle with performance limitations, developer friction, and fragmented ecosystems. As decentralized applications expand into areas such as finance, gaming, and real time data systems, the underlying infrastructure must support higher throughput, lower latency, and consistent execution environments. Fogo is a Layer 1 blockchain designed to address these infrastructure challenges by using the Solana Virtual Machine as its execution environment while building a separate network optimized for performance, reliability, and scalability.
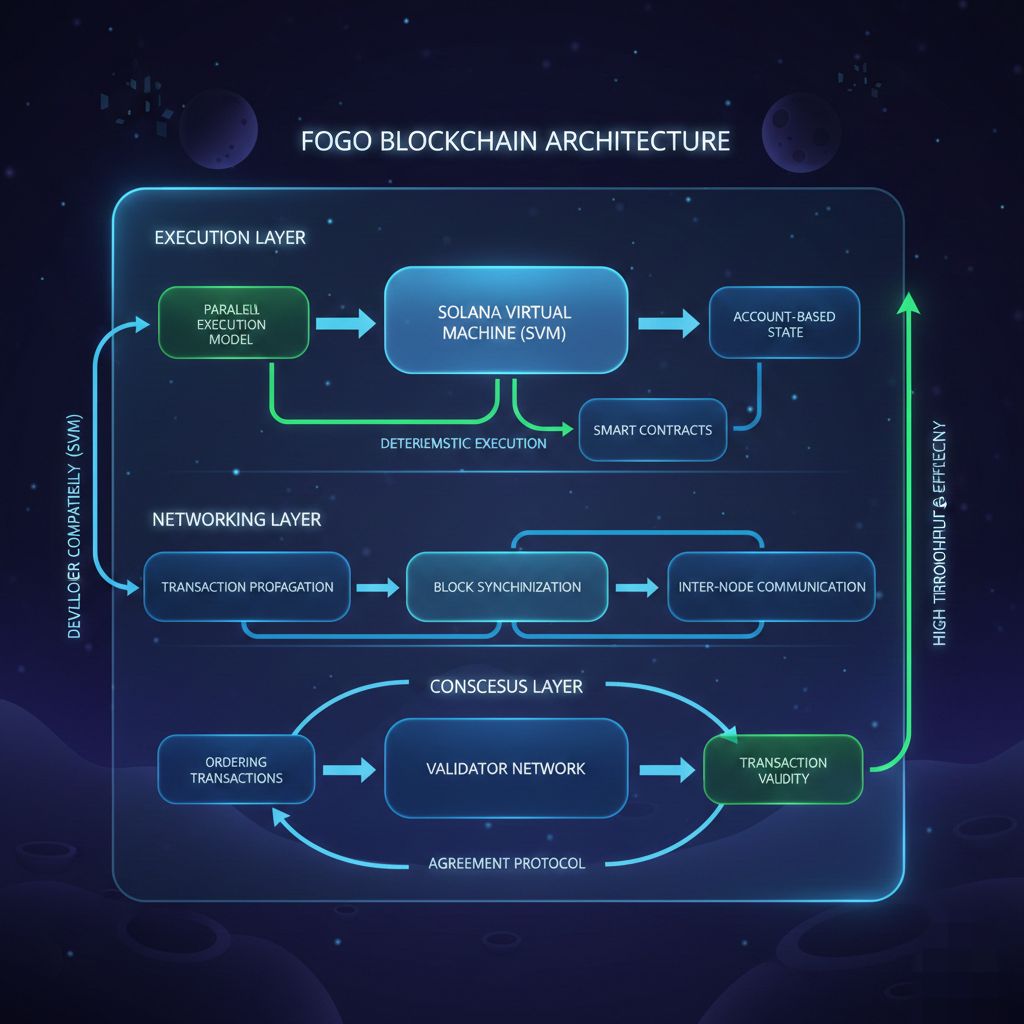
One of the core problems Fogo is trying to solve is the trade off between performance and compatibility. Many blockchains offer unique performance improvements, but they introduce entirely new virtual machines, programming languages, or execution environments. This creates barriers for developers who must learn new tools and rewrite applications. On the other hand, networks that prioritize compatibility sometimes inherit performance limitations. Fogo attempts to solve this by combining a proven execution model with a new network architecture designed specifically for high throughput and efficiency. By using the Solana Virtual Machine, Fogo enables developers to use familiar tools and execution logic while benefiting from infrastructure improvements at the network level.
At a high level, Fogo works as a standalone Layer 1 blockchain that integrates the Solana Virtual Machine to execute smart contracts and transactions. The Solana Virtual Machine, often called SVM, is responsible for processing instructions, managing account states, and ensuring deterministic execution of programs. Unlike virtual machines that process transactions sequentially, the SVM supports parallel execution. This means multiple transactions can be processed at the same time, as long as they do not modify the same state. Fogo leverages this capability while optimizing other parts of the blockchain stack, such as transaction propagation, validation, and consensus coordination, to reduce delays and increase throughput.
The key functional advantage of using the Solana Virtual Machine is its account based parallel execution model. In this model, transactions explicitly declare which accounts they will read from and write to. This allows the network to safely execute independent transactions in parallel. Fogo uses this model to improve processing efficiency, reduce bottlenecks, and maintain predictable performance under heavy load. This is particularly important for applications that require real time responsiveness, such as trading platforms, multiplayer games, and high frequency transaction systems.
From an architectural perspective, Fogo separates execution from other infrastructure layers while maintaining compatibility with the Solana Virtual Machine specification. The execution layer focuses on running programs, verifying transaction logic, and updating blockchain state. The networking layer handles communication between nodes, including transaction propagation and block synchronization. The consensus layer ensures agreement among validators on the order and validity of transactions. By optimizing these layers individually, Fogo aims to improve overall network efficiency without changing how developers interact with the execution environment.
Another important design consideration is deterministic execution and state consistency. Deterministic execution means that every validator processes the same transaction and reaches the same result. This is essential for maintaining trust and ensuring that the blockchain remains consistent across all nodes. Because Fogo uses the Solana Virtual Machine, it inherits a deterministic execution model that ensures reliable and predictable results. This is particularly valuable in applications such as decentralized finance, where incorrect execution could result in financial losses or system instability.
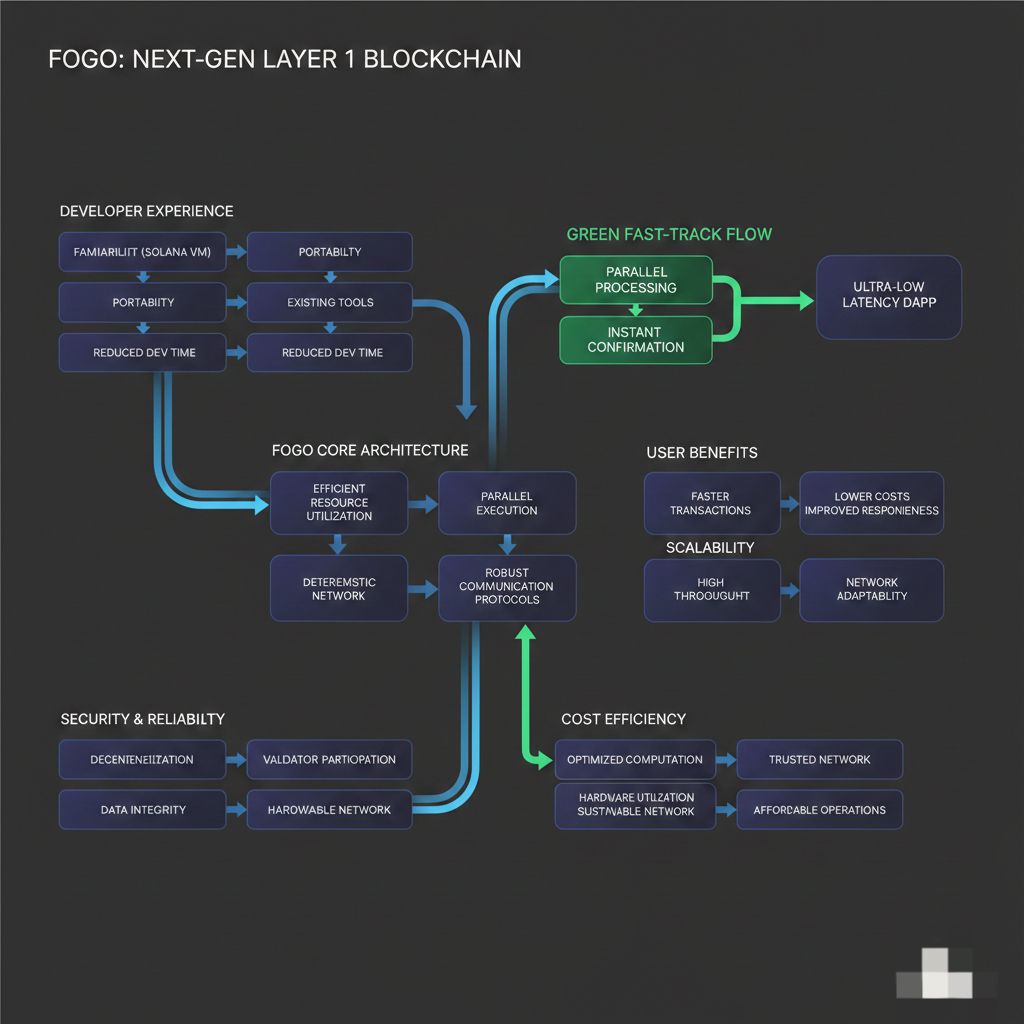
From a developer perspective, Fogo provides familiarity and portability. Developers who already understand Solana programs can deploy similar logic on Fogo without needing to learn a completely new virtual machine. This reduces development time and lowers the barrier to entry. It also allows existing tools, compilers, and frameworks designed for the Solana Virtual Machine to work with minimal modification. This compatibility enables developers to focus on building applications rather than adapting to new infrastructure.
For users, the benefits of Fogo are often indirect but important. Faster transaction processing means lower waiting times for confirmations. Efficient execution reduces network congestion and improves application responsiveness. Lower infrastructure overhead can also lead to reduced transaction costs. These improvements enhance the overall user experience, even if users are not aware of the underlying technical architecture.
Fogo also addresses scalability challenges through efficient resource utilization and parallel processing. Traditional blockchains process transactions sequentially, which limits throughput as network activity increases. In contrast, Fogo uses parallel execution to process multiple transactions simultaneously. This allows the network to scale more effectively as demand grows. Additionally, efficient networking and validation mechanisms help reduce latency, allowing transactions to be confirmed more quickly.
Security and reliability remain fundamental aspects of any Layer 1 blockchain. Fogo relies on validator nodes to verify transactions and maintain network consensus. Validators check transaction validity, execute programs using the Solana Virtual Machine, and ensure that state changes are correct. The deterministic nature of execution reduces the risk of inconsistent results between validators. Network security also depends on decentralization, validator participation, and robust communication protocols that prevent data loss or manipulation.
Cost efficiency is another important aspect of Fogo’s design. Efficient execution reduces the computational resources required per transaction. Parallel processing improves hardware utilization, allowing nodes to process more transactions without proportional increases in cost. This can make the network more sustainable and accessible over time. Lower operational overhead can also benefit developers who deploy applications that require frequent interactions with the blockchain.
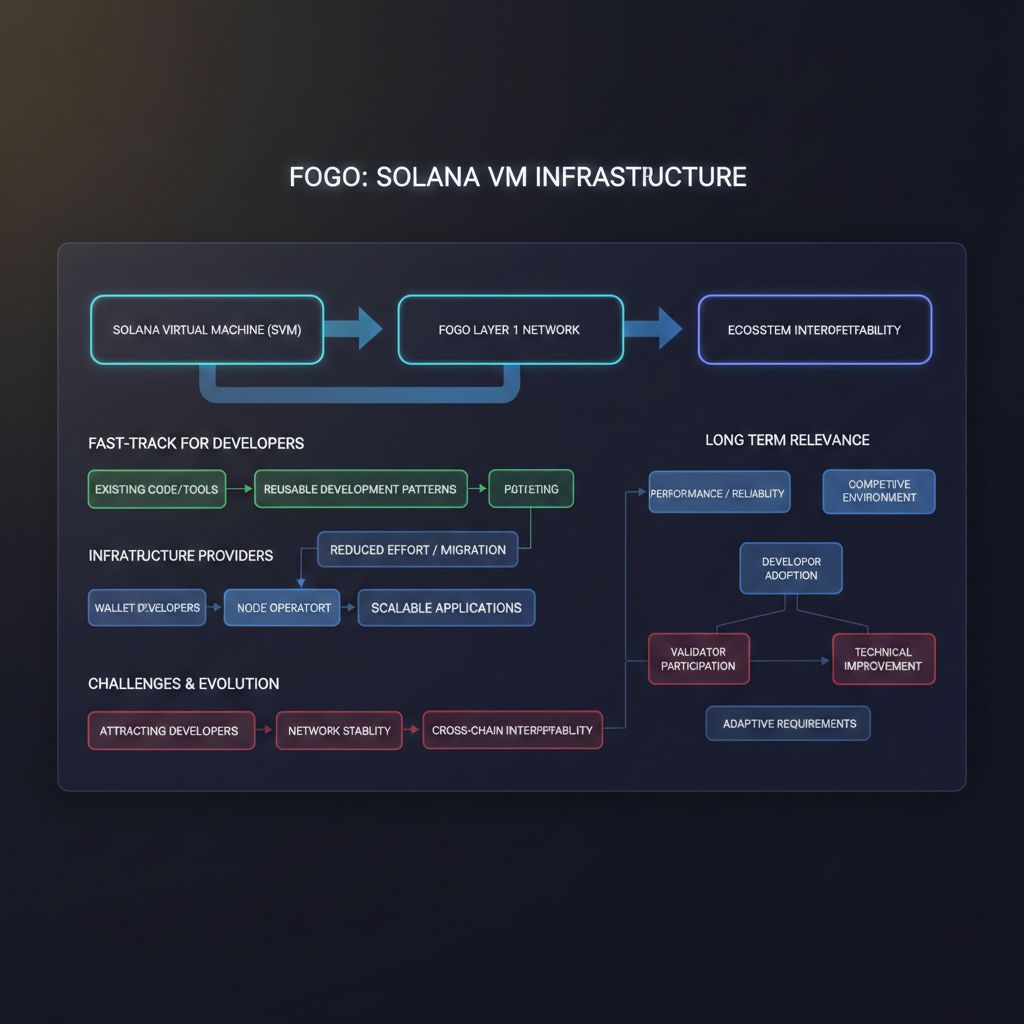
Fogo’s compatibility with the Solana Virtual Machine also improves ecosystem interoperability. Developers can reuse existing code, tools, and development patterns. This helps avoid fragmentation and reduces the effort required to build or migrate applications. It also makes it easier for infrastructure providers, such as wallet developers and node operators, to support the network.
The long term relevance of Fogo depends on its ability to maintain performance, reliability, and developer adoption in a competitive environment. The blockchain ecosystem includes many Layer 1 networks, each offering different trade offs between scalability, decentralization, and compatibility. Fogo’s approach focuses on improving infrastructure efficiency while maintaining compatibility with a widely used execution environment. However, it must also ensure strong validator participation, network stability, and continuous technical improvement to remain competitive.
Challenges may include attracting developers, building ecosystem tools, and ensuring decentralization as the network grows. Performance improvements must be balanced with security and reliability. Infrastructure networks must also adapt to evolving requirements, such as cross chain interoperability, data availability, and changing application demands.
Overall, Fogo represents an infrastructure focused approach to blockchain design. By using the Solana Virtual Machine within a new Layer 1 network, it combines execution compatibility with infrastructure level optimization. This allows developers to build scalable applications while benefiting from efficient execution and predictable performance. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, networks like Fogo contribute to the broader effort of building reliable, scalable, and efficient decentralized computing platforms.
