@Vanarchain Blockchain technology has introduced new ways to manage digital ownership, identity, and decentralized applications, but adoption outside the crypto-native audience remains limited. Many blockchain networks are complex for users, expensive to operate at scale, and difficult for developers to integrate into mainstream products such as games, media platforms, and brand ecosystems. These limitations create friction that prevents Web3 from reaching broader audiences. Vanar is a Layer 1 blockchain built to address these challenges by focusing on usability, scalability, and integration with real-world applications such as gaming, entertainment, artificial intelligence, and brand platforms.
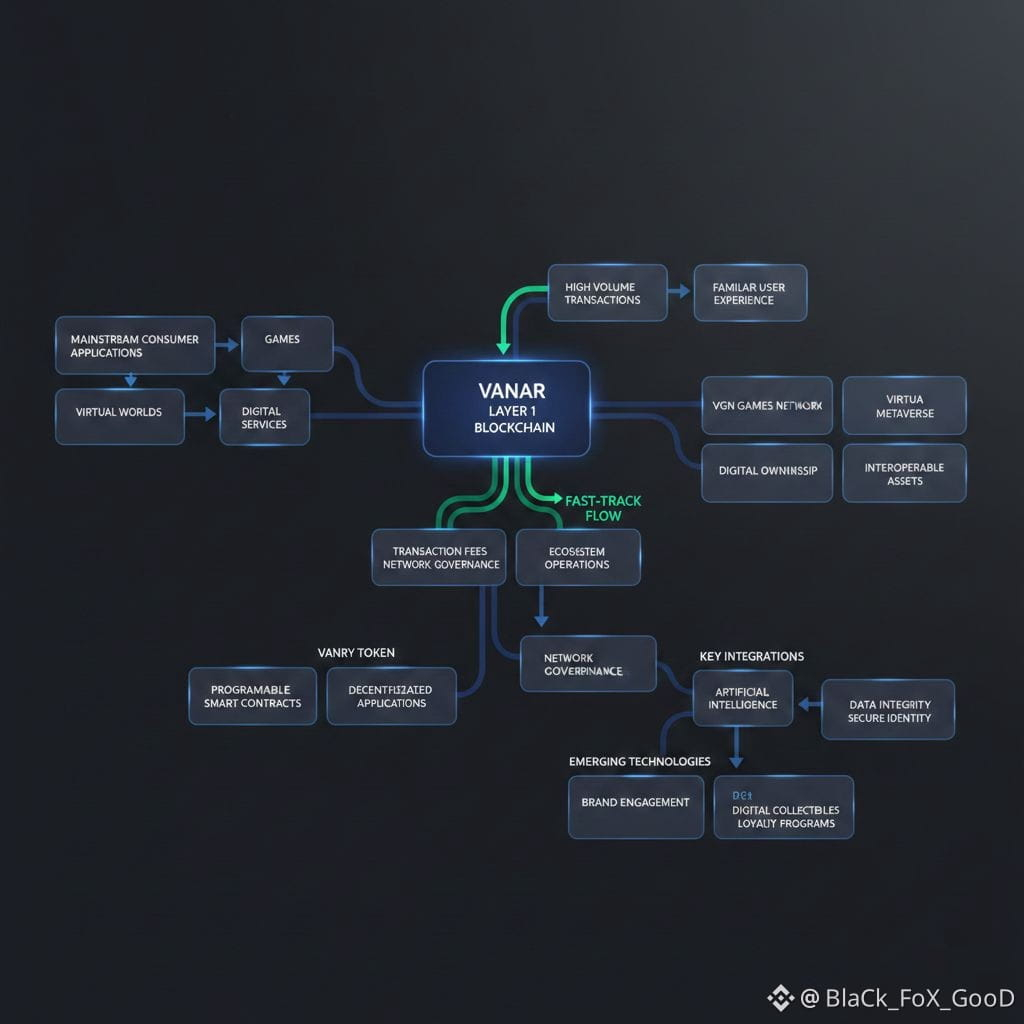
The core problem Vanar aims to solve is the gap between blockchain infrastructure and mainstream consumer applications. Traditional blockchains often prioritize decentralization and security, but they may lack the performance, ease of integration, and user experience required by large-scale consumer platforms. As a result, developers building games, virtual worlds, or digital services often face technical barriers when trying to incorporate blockchain features such as digital ownership or token economies. Users, in turn, may struggle with wallet management, high transaction fees, or slow performance. Vanar attempts to reduce these barriers by providing infrastructure designed specifically for high volume consumer environments.
At a high level, Vanar operates as a Layer 1 blockchain, which means it functions as its own independent network responsible for validating transactions, securing data, and executing smart contracts. The network uses its native token, VANRY, to power transactions, pay network fees, and support ecosystem operations. Like other modern blockchains, Vanar supports programmable smart contracts, allowing developers to build decentralized applications that automate logic without relying on centralized intermediaries. These smart contracts can manage digital assets, enforce rules, and enable interactions between users and applications.
Vanar’s system design focuses on supporting applications that require fast response times and scalable infrastructure. Gaming platforms and virtual environments, for example, generate a large number of small transactions, such as asset transfers, achievements, or in game interactions. A blockchain designed for these environments must process transactions efficiently without causing delays or excessive costs. Vanar addresses this by optimizing its network for performance and integrating features that allow applications to interact with blockchain services without exposing users to unnecessary technical complexity. This approach allows developers to incorporate blockchain functionality while maintaining familiar user experiences.
One of the key features of Vanar is its integration with platforms such as the Virtua Metaverse and the VGN games network. These platforms demonstrate how blockchain can support digital ownership of virtual items, identities, and assets. Instead of storing these assets on centralized servers, blockchain ensures that ownership records are transparent and verifiable. This model allows users to retain control over their digital items across different applications and environments. For developers, this creates opportunities to build interoperable ecosystems where assets can move between games, platforms, or virtual spaces.
Vanar also focuses on compatibility with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and brand engagement platforms. Artificial intelligence systems often rely on large volumes of data and automated interactions, which can benefit from transparent and verifiable infrastructure. Blockchain can help ensure the integrity of data, track digital ownership, and provide secure identity frameworks. Similarly, brands can use blockchain to manage digital collectibles, loyalty programs, and virtual experiences in a way that ensures authenticity and traceability.
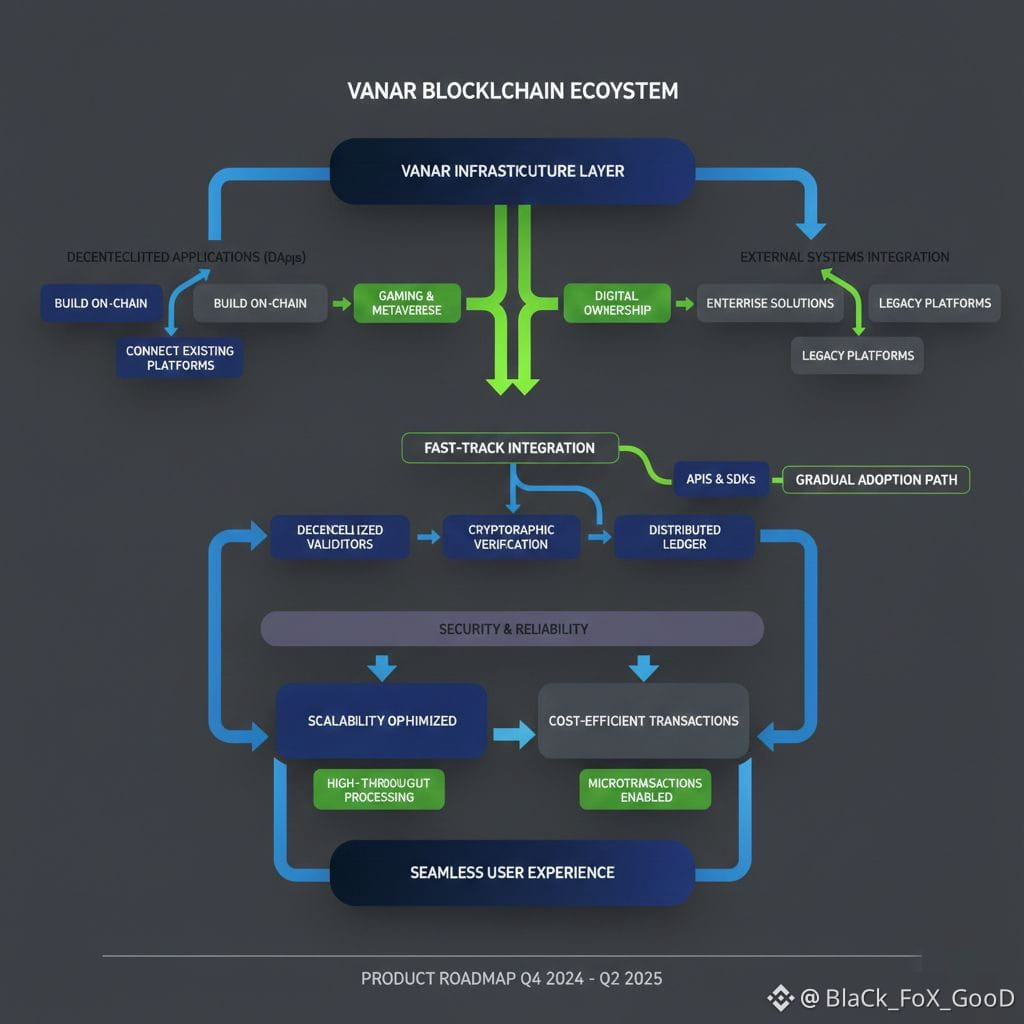
From an architectural perspective, Vanar functions as a foundational infrastructure layer that supports decentralized applications while remaining flexible enough to integrate with external systems. Developers can build applications directly on the blockchain or connect existing platforms using application programming interfaces and software development tools. This allows companies to adopt blockchain gradually without redesigning their entire systems. For users, much of this infrastructure remains invisible, allowing them to interact with applications without needing deep technical knowledge of blockchain mechanics.
Security and reliability are essential aspects of any blockchain network. Vanar relies on its decentralized validator system to confirm transactions and maintain the integrity of the network. Each transaction is verified and recorded on a distributed ledger, reducing the risk of data manipulation or unauthorized changes. The use of cryptographic verification ensures that only valid transactions are accepted, and the decentralized nature of the network reduces dependence on a single point of control. This model increases transparency and trust, particularly in applications involving digital ownership or financial value.
Scalability is another important focus area for Vanar. Consumer applications such as games and virtual environments require infrastructure that can support large numbers of users simultaneously. Traditional blockchains may struggle with congestion when usage increases, leading to slow transactions and higher fees. Vanar’s design aims to maintain consistent performance even under heavy usage. This allows developers to build applications with the expectation that the network can handle growth without significant performance degradation.
Cost efficiency is closely related to scalability and usability. High transaction fees can make blockchain impractical for everyday applications, especially in gaming or digital media environments where frequent interactions occur. By optimizing its network structure and transaction handling, Vanar aims to keep transaction costs manageable. This allows developers to implement blockchain features without creating financial barriers for users. Lower costs also support microtransactions and frequent asset interactions, which are common in interactive digital platforms.
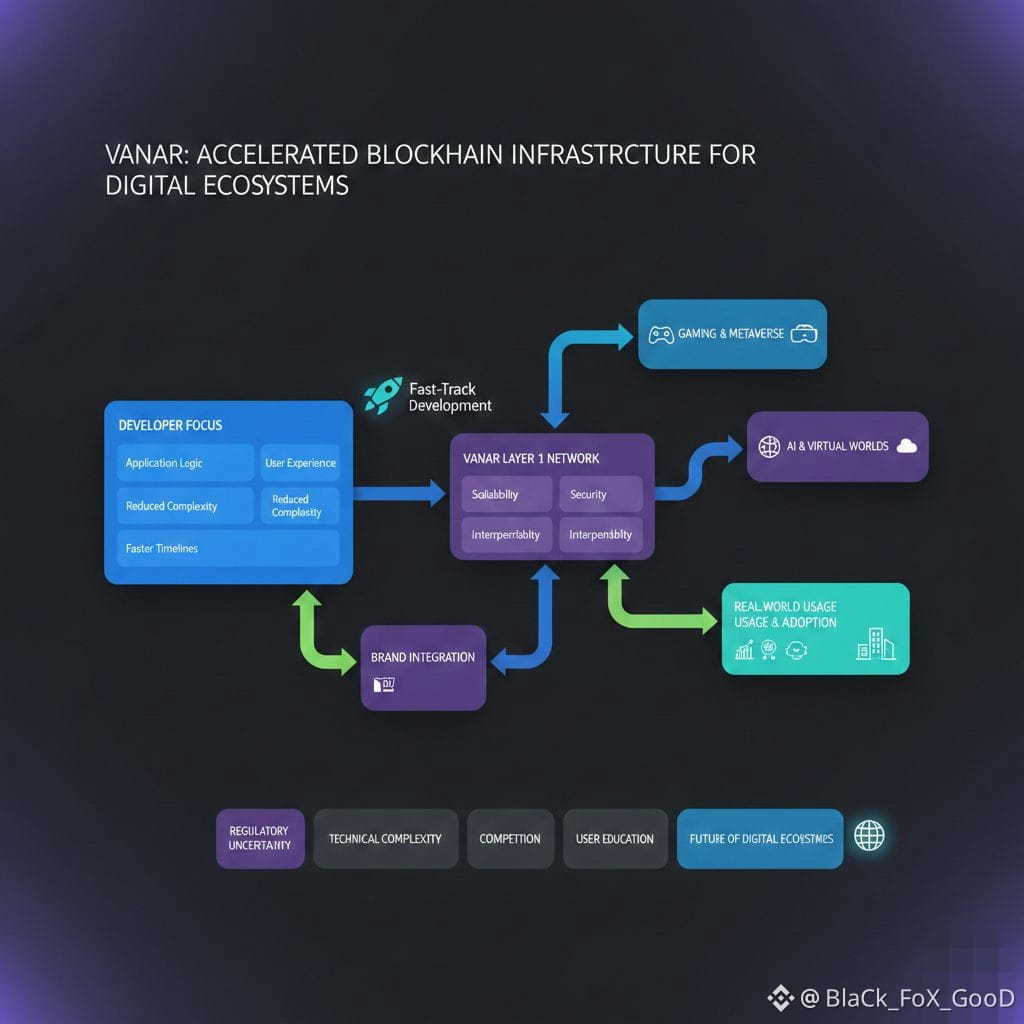
From a developer perspective, Vanar provides infrastructure that reduces the complexity of integrating blockchain into applications. Developers can focus on application logic and user experience rather than managing the underlying network. This can accelerate development timelines and reduce technical barriers to entry. For users, the benefits may not always be visible, but they can experience improved asset ownership, better security, and more transparent systems without needing to understand the underlying blockchain.
Vanar’s long term relevance depends on its ability to compete with other Layer 1 blockchains that also target scalability and mainstream adoption. The blockchain ecosystem includes many networks with similar goals, and success often depends on developer adoption, ecosystem growth, and real world usage. Vanar’s focus on gaming, metaverse environments, and brand integration positions it within sectors that have strong potential for blockchain adoption. However, it must continue to demonstrate reliability, performance, and developer support to remain competitive.
At the same time, challenges remain for all blockchain platforms seeking mainstream adoption. These include regulatory uncertainty, technical complexity, and competition from both decentralized and centralized technologies. User education and seamless integration are critical factors that determine whether blockchain infrastructure becomes widely used. Networks like Vanar must continue improving usability and interoperability while maintaining security and decentralization.
Vanar represents an example of how blockchain infrastructure is evolving beyond financial applications toward broader digital ecosystems. By focusing on scalability, usability, and integration with real world platforms, it aims to support applications that require reliable and transparent digital infrastructure. Its role as a Layer 1 network provides the foundation for decentralized applications, digital ownership, and interactive virtual environments. Whether used in gaming, brand engagement, artificial intelligence, or virtual worlds, the underlying goal is to provide infrastructure that makes blockchain practical and accessible for everyday digital experiences.
