Introduction:
Solana is a high-performance, open-source blockchain network designed to support decentralized applications (dApps), decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, and Web3 projects. Launched in 2020 by Anatoly Yakovenko, Solana aims to solve the scalability limitations faced by earlier blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
The native cryptocurrency of the network is SOL, which is used to pay transaction fees, participate in staking, and secure the network.
How Solana Works:
Solana combines two key consensus mechanisms:
1. Proof of Stake (PoS):
Validators stake SOL tokens to help secure the network and validate transactions.
2. Proof of History (PoH):
Proof of History is Solana’s unique innovation. It timestamps transactions before they are confirmed, allowing the network to process transactions more efficiently and at very high speeds.
This combination enables Solana to process thousands of transactions per second while maintaining low fees.
Key Features of Solana:
High Transaction Speed:
Solana is known for its extremely high throughput, capable of processing thousands of transactions per second under optimal conditions.
Low Transaction Fees:
Transaction costs on Solana are typically a fraction of a dollar, making it attractive for developers building scalable applications.
Expanding Ecosystem:
The Solana ecosystem includes:
Decentralized exchanges
NFT marketplaces
Web3 gaming platforms
Infrastructure and developer tools
Solana Logo and Coin Visuals:
Below are representative visuals commonly used in presentations and articles about Solana:

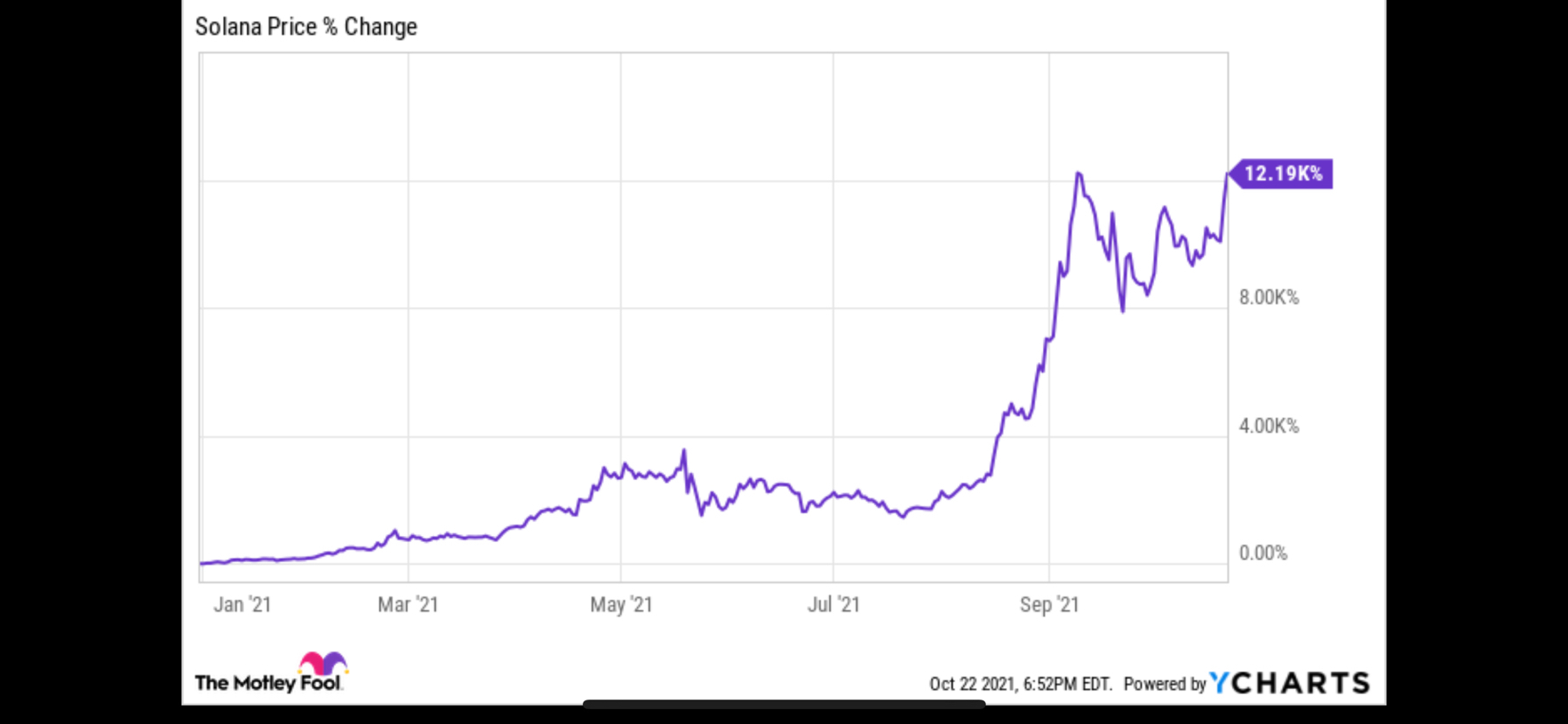
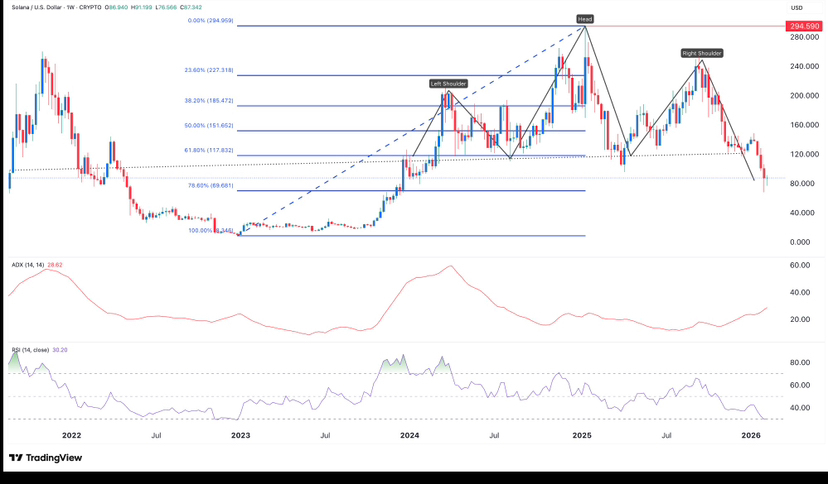
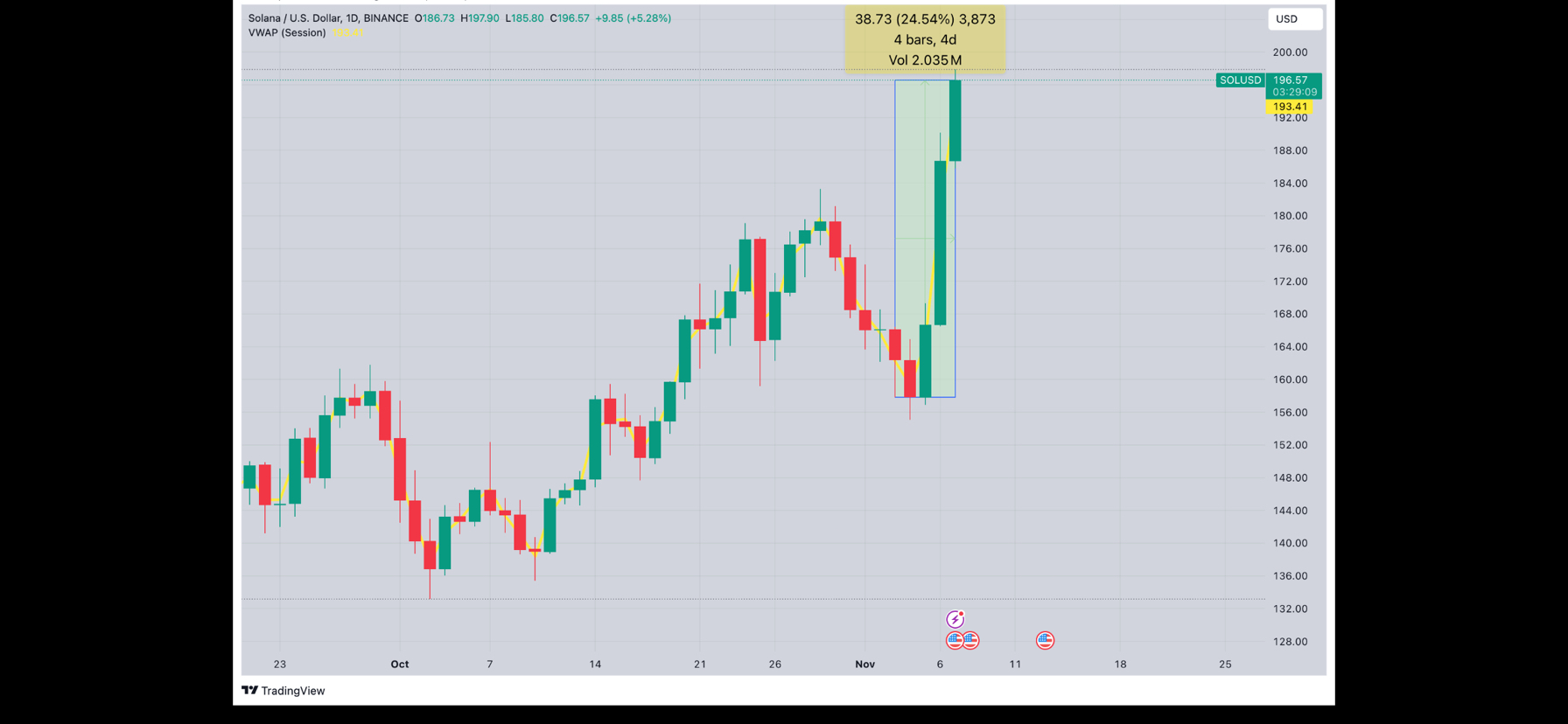
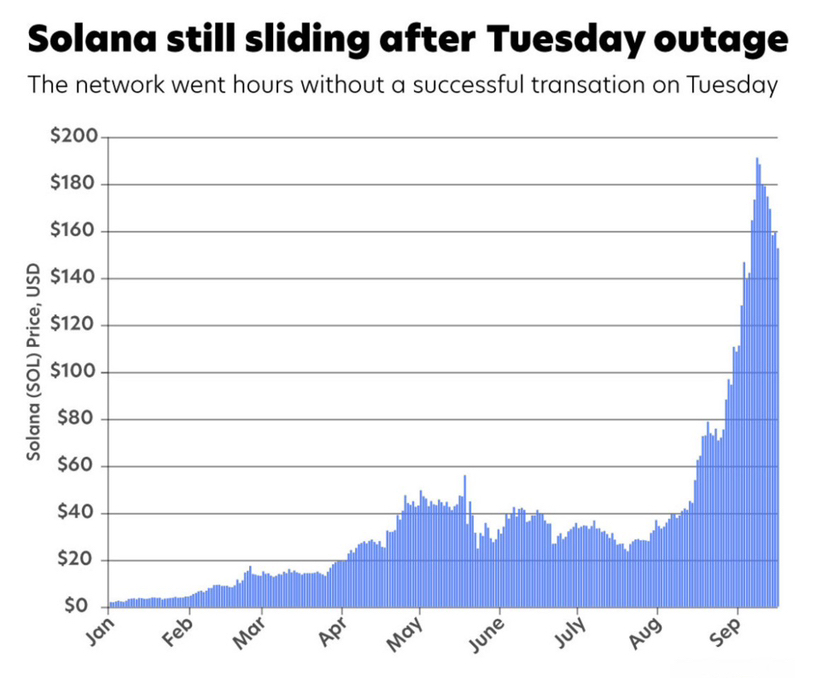
Price Performance and Market Position:
Solana has experienced significant price volatility since launch. During major crypto bull markets, SOL reached substantial highs and became one of the top cryptocurrencies by market capitalization.
Like most cryptocurrencies, its price fluctuates based on:
Market demand
Network activity
Broader crypto market trends
Regulatory developments
Investors should always conduct independent research and understand the risks associated with cryptocurrency investments.
Comparison with Other Blockchains:
Compared with Ethereum:
Solana offers faster transaction speeds.
Solana generally has lower fees.
Ethereum has a longer track record and larger developer community.
Compared with Bitcoin:
Bitcoin is primarily designed as a store of value.
Solana is optimized for smart contracts and decentralized applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
High scalability
Low transaction costs
Rapid ecosystem growth
Strong developer activity
Disadvantages:
Market volatility
Network outages in past years
Competition from other smart-contract platforms
Conclusion:
Solana has established itself as one of the leading smart-contract platforms in the cryptocurrency market. Its combination of speed, low fees, and innovative Proof of History mechanism makes it a strong competitor in the blockchain space.
However, like all cryptocurrencies, SOL carries investment risk due to price volatility and evolving market conditions.