$BNB ||
Introduction:
In the fast-evolving world of cryptocurrency, few digital assets have grown as rapidly and strategically as BNB. Originally launched as a utility token for a crypto exchange, BNB has transformed into a major blockchain asset powering an entire ecosystem of decentralized applications, financial services, and digital innovation.
From its early days priced under $2 to becoming one of the largest cryptocurrencies by market capitalization, BNB’s journey reflects the broader expansion of blockchain technology itself.
Origins of BNB:
BNB was launched in July 2017 by the cryptocurrency exchange Binance. The exchange was founded by Changpeng Zhao (commonly known as CZ).
Initially, BNB was created as an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain. Its main purpose was simple:
Offer discounted trading fees
Provide access to token sales on Binance Launchpad
Incentivize user engagement on the Binance platform
However, as Binance grew into the world’s largest crypto exchange by trading volume, the utility and demand for BNB expanded dramatically.

Migration to BNB Chain:
In 2019, Binance launched its own blockchain network, moving BNB off Ethereum. Today, BNB powers:
BNB Chain
BNB Smart Chain
The ecosystem supports:
Smart contracts
Decentralized applications (dApps)
DeFi protocols
NFTs
Gaming platforms
This transformation shifted BNB from being merely an exchange utility token to becoming a core infrastructure asset.
Tokenomics & Supply Mechanics:
One of the most important features of BNB is its deflationary model.
Quarterly Token Burns:
Binance commits to using a portion of its profits to buy back and permanently destroy (burn) BNB tokens.
Goal:
Reduce total supply from 200 million tokens to 100 million.
This reduction in supply can increase scarcity over time, which may positively impact price (though this is not guaranteed).
Historical Price Performance:
BNB’s growth has been remarkable:
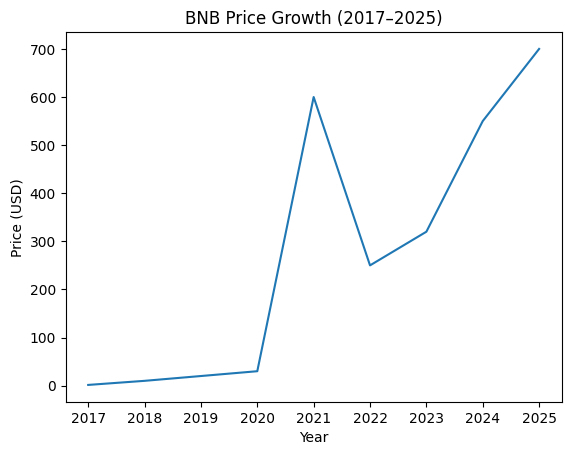
Major Use Cases of BNB:
BNB is far more than a speculative asset. Its use cases include:
1. Trading Fee Discounts:
Users on Binance receive reduced fees when paying with BNB.
2. Gas Fees on BNB Chain:
BNB is used to pay transaction fees on BNB Smart Chain.
3. Launchpad Participation:
Investors use BNB to access new token sales.
4. DeFi & Staking:
BNB is widely used in decentralized finance applications for lending, liquidity provision, and staking.
5. Real-World Payments:
Some platforms accept BNB for travel bookings, gift cards, and online services.
Competitive Position:
BNB competes with major blockchain assets like:
While Bitcoin focuses on being a store of value, and Ethereum focuses on decentralized applications, BNB combines exchange utility with smart contract functionality — giving it a hybrid advantage.
Advantages of BNB:
1. Strong backing from the world’s largest exchange
2.Deflationary token burn model
3.Large and active ecosystem
4.Lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum
5.Wide integration across DeFi and Web3 projects
Risks & Challenges:
Like all cryptocurrencies, BNB carries risks:
1.Regulatory scrutiny on exchanges
2.Market volatility
3.Competition from other blockchains
4.Security vulnerabilities in DeFi projects
5.Crypto markets can be unpredictable, and prices can fluctuate rapidly.
Future Outlook:
The long-term outlook of BNB depends on:
Continued adoption of BNB Chain
Regulatory clarity worldwide
Growth of decentralized finance
Binance’s operational stability
If the ecosystem continues expanding, BNB could maintain its position as a leading digital asset. However, investors should always conduct independent research before making financial decisions.
#bullish #Binance #BNB_Market_Update #ETHETFsApproved #BTC走势分析