XRP is the native asset of the XRP Ledger (XRPL), a network designed for fast and cost-effective payments globally. Unlike Bitcoin, which uses mining and seeks maximum decentralization, XRP was created with the goal of integrating with the traditional financial system, facilitating the connection between institutions and blockchain technology.
The XRPL uses a consensus mechanism without mining, which reduces energy consumption and allows for low transaction fees. Transactions settle in 3-5 seconds, with minimal costs usually just 0.00001 XRP, equivalent to a fraction of a cent.
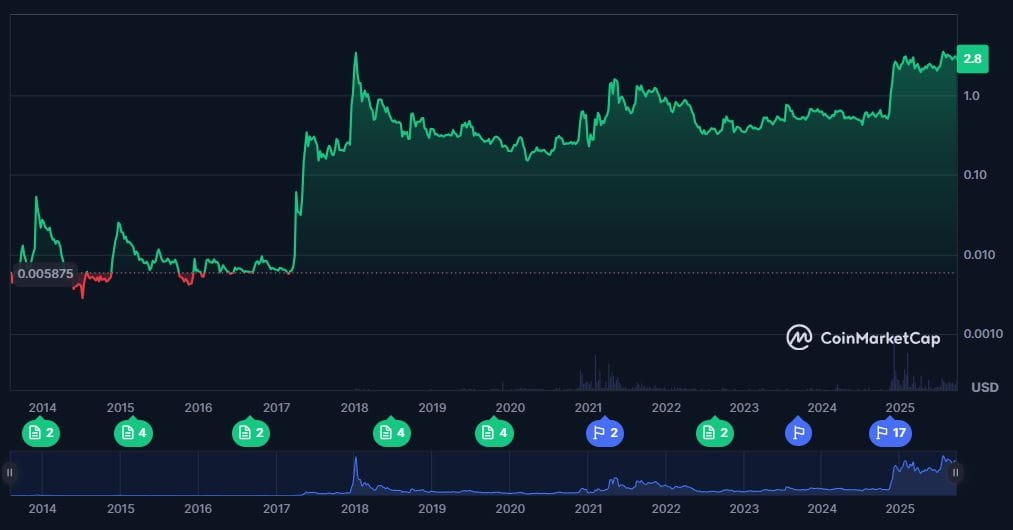
As of September 2025, XRP's price is expected to be between $2.80 and $3.00, with a market cap of around $170-180 billion, placing it among the largest cryptocurrencies by market size.
History and Creators of XRP

In 2004, Canadian developer Ryan Fugger created RipplePay, a trust-based payment system intended as an alternative to the traditional banking system.
A few years later, in 2011, Jed McCaleb, the initial founder of Mt. Gox and creator of the eDonkey file-sharing network, began working with other developers on a global, mining-free payment network designed to be more efficient and cheaper than Bitcoin.
In 2012, McCaleb partnered with Chris Larsen, an entrepreneur with extensive experience in fintech and former CEO of E-Loan and Prosper. That same year, they founded the San Francisco-based company OpenCoin. The team was completed by Arthur Britto and David Schwartz, who designed the architecture of the XRP Ledger and wrote its original whitepaper.
That year, all 100 billion XRP coins were created in one go, establishing the entire supply from scratch without the need for mining. This approach marked a key difference from Bitcoin and other proof-of-work-based cryptocurrencies.
In 2013, OpenCoin changed its name to Ripple Labs, and later, in 2015, to simply Ripple. To avoid confusion between the company and the token, the use of the acronym XRP as the official name of the asset was reinforced starting in 2018. Since then, Ripple's vision has been clear: to connect the traditional financial system with blockchain technology, enabling fast, secure, and low-cost international transfers.
XRP and the Blockchain Trilemma
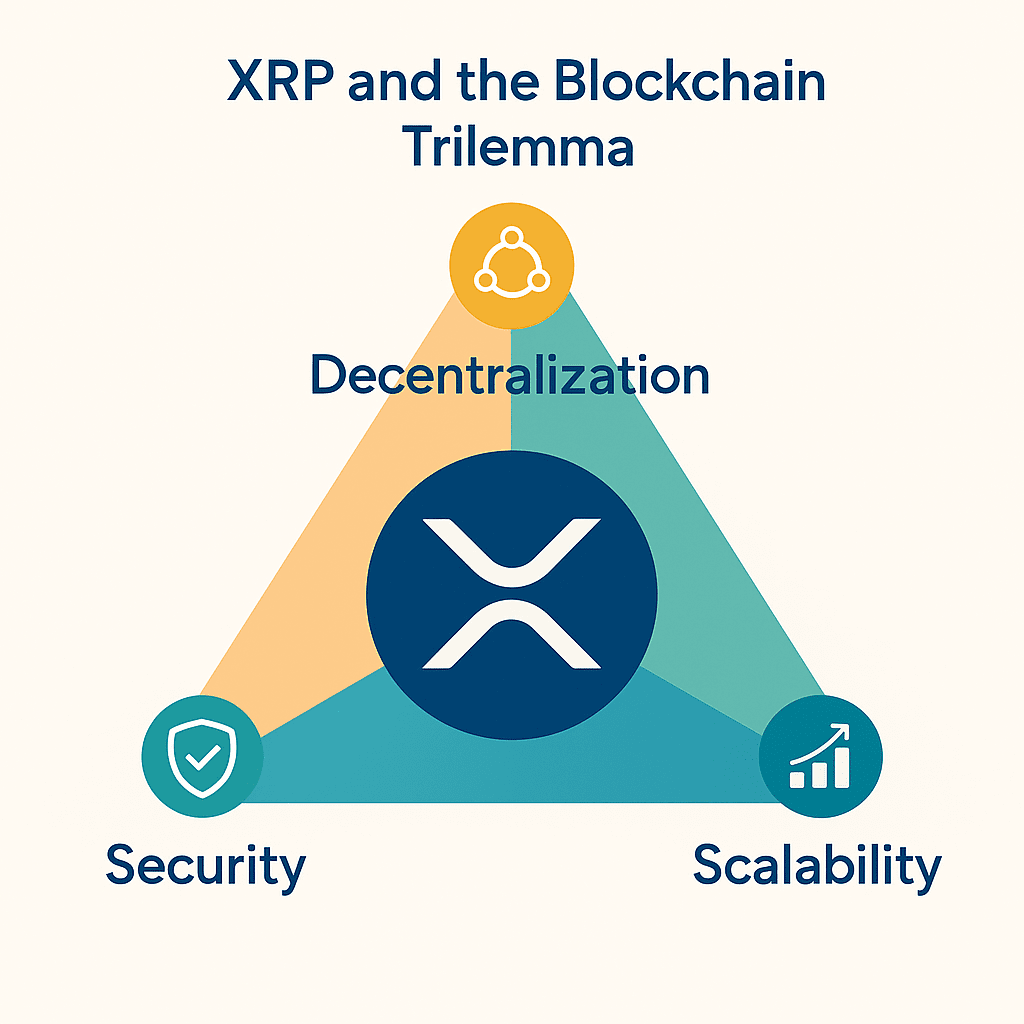
The blockchain trilemma poses the challenge of balancing three key properties: decentralization, security, and scalability. XRP has taken a very unique approach to this challenge:
Decentralization – Moderate ⚠️
While anyone can run a node, the main validator list (UNL) is managed by Ripple and strategic partners. This improves efficiency and speed, but involvessmaller openingthan other networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Security – High ✅
Its consensus mechanism prevents attacks such as51% attack. Since 2012,There have been no hacks or serious outageson the network, which demonstrates its strength and reliability.Scalability – Very High 🚀
The XRPL processes up to1,500 transactions per second, with confirmations in3-5 secondsand extremely low costs. This makes it ideal forglobal payments and remittances, competing with systems such as Visa and SWIFT.
In short, XRP prioritizes scalability and security, sacrificing some decentralization. This makes it an attractive solution for banks and financial institutions, although less open than purely decentralized blockchains like Bitcoin.
Path
The history of XRP has been marked by technological advancements, gradual adoption, and regulatory challenges.
In 2014, Ripple began collaborating with financial institutions to optimize cross-border payments. While some banks tested its technology, adoption of XRP as an asset was limited in the early years.
In 2015, Ripple Labs faced its first major regulatory challenge when FinCEN fined it $700,000 for operating as an unregistered money services business and for deficiencies in its anti-money laundering (AML) program. This event marked an important precedent in the relationship between cryptocurrencies and regulators in the U.S.
The turning point came in December 2020, when the SEC sued Ripple, alleging that the sale of XRP constituted an unregistered security offering. This process generated significant uncertainty and affected both the project's price and reputation.
You can check the real-time XRP quote on coinmarketcap:
https://coinmarketcap.com/currencies/xrp/
After years of litigation, the court issued a landmark ruling in July 2023:
Institutional sales: considered investment contracts and therefore subject to regulation as securities.
Programmatic sales on exchanges: not classified as securities.
Other distributions, such as payments for services, were also not considered securities.
Finally, in August 2025, the case was closed, with Ripple agreeing to pay a $125 million fine. The ruling confirmed that XRP is not a security in secondary transactions, although institutional sales will remain under regulatory oversight. This outcome provided greater clarity and confidence, pushing the price of XRP above $3 by September 2025.
In parallel, Ripple implemented an escrow system in 2017 to transparently manage the 55 billion XRP the company held. Up to 1 billion tokens are released each month, with unused tokens returned to escrow, bringing predictability to the market.
Currently, the XRPL processes around 1,500 transactions per second and is the foundation of On-Demand Liquidity (ODL), a service that enables 24/7 international settlements. These innovations have positioned XRP as one of the most relevant tools for global payments in the blockchain world.
Future and Price of$XRP

The future of XRP looks promising thanks to the regulatory clarity gained following the SEC case and the growing integration of its ecosystem into traditional finance.
One of the most significant milestones occurred on September 18, 2025, with the launch of the REX-Osprey XRP ETF (XRPR) in the United States. This fund allows institutional and retail investors to gain regulated exposure to the spot price of XRP, comparable to existing Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs. Its structure complies with U.S. law, being registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940 and having a subsidiary in the Cayman Islands for its operations.
The ETF's debut was well-received, with significant trading volume on its first day, reflecting the growing institutional interest in XRP. This launch represents an important step toward legitimizing and expanding the market.
In parallel, Ripple has developed RLUSD, a stablecoin backed 1:1 by US dollars. This stablecoin is integrated into platforms like MoonPay, facilitating its use for payments, transfers, and real-time settlements via XRPL. Its incorporation reinforces Ripple's vision of connecting traditional banking with blockchain technology.
Currently, XRPL maintains its capacity of 1,500 transactions per second, with rapid settlements and minimal costs. These characteristics make it ideal for international payments and remittances, a global market valued at hundreds of billions of dollars. With the momentum of RLUSD and the XRPR ETF, more businesses and financial institutions are expected to adopt XRP-based solutions.
While XRP's price remains volatile, analysts emphasize that the combination of institutional adoption, clear regulation, and technological development positions XRP as one of the projects with the greatest potential for long-term growth. However, its evolution will depend on macroeconomic factors, global regulatory changes, and Ripple's ability to continue innovating.
Conclusion
XRP has established itself as a bridge between traditional finance and the blockchain world, offering a technology designed for fast, secure, and efficient payments. From its origins in RipplePay to its current role, it has demonstrated resilience and innovation, overcoming regulatory and technological challenges for over a decade.
The resolution of the SEC case and the launch of the first XRP ETF have marked a new era for the project, paving the way for greater legitimacy and integration with the traditional financial system. Furthermore, the growth of RLUSD and other XRPL-based solutions reinforces its role as a key player in the evolution of digital payments.
Despite these advances, XRP faces challenges such as competition from other networks and possible changes in international regulation. Its future will depend on the trust of banks, businesses, and users, as well as Ripple's ability to attract more developers and expand its ecosystem.
With a solid foundation, real utility, and an institutional-focused strategy, XRP has the potential to consolidate itself as one of the most relevant digital assets in the long term. However, as with any cryptocurrency investment, it is essential to exercise caution and risk management, balancing growth opportunities with the market's inherent volatility.
#XRP #Ripple #Blockchain #CBDC #Satoshifactory