Fogo began with a challenging premise: must decentralization always come at the expense of speed? For a long time, blockchain innovation seemed caught between two competing priorities. On one side stood the commitment to openness, permissionless access, and global participation. On the other was the expectation of efficiency and reliability already common in traditional financial systems. Fogo emerged from the belief that these objectives do not have to contradict each other.
Rather than introducing another conventional Layer 1 blockchain that mirrors existing designs, Fogo set out to reconsider how performance and decentralization might operate together within a single architecture.
In the early development of decentralized finance, technical constraints quickly became evident. Even leading blockchains struggled with delays and execution bottlenecks. Traders coming from traditional finance identified a key weakness: decentralized platforms would struggle to compete with centralized exchanges if users experienced noticeable latency.
This realization shaped the thinking of Fogo’s early contributors. They envisioned infrastructure capable of delivering near real-time responsiveness without sacrificing core principles such as openness and censorship resistance. Developed by individuals with experience in financial markets, Fogo aims to recreate institutional-level trade execution inside a decentralized framework. Instead of treating decentralization and speed as opposing forces, the project explores how both can be engineered simultaneously. From the beginning, its mission has centered on building the strongest possible on-chain trading environment by tailoring infrastructure to performance-sensitive applications.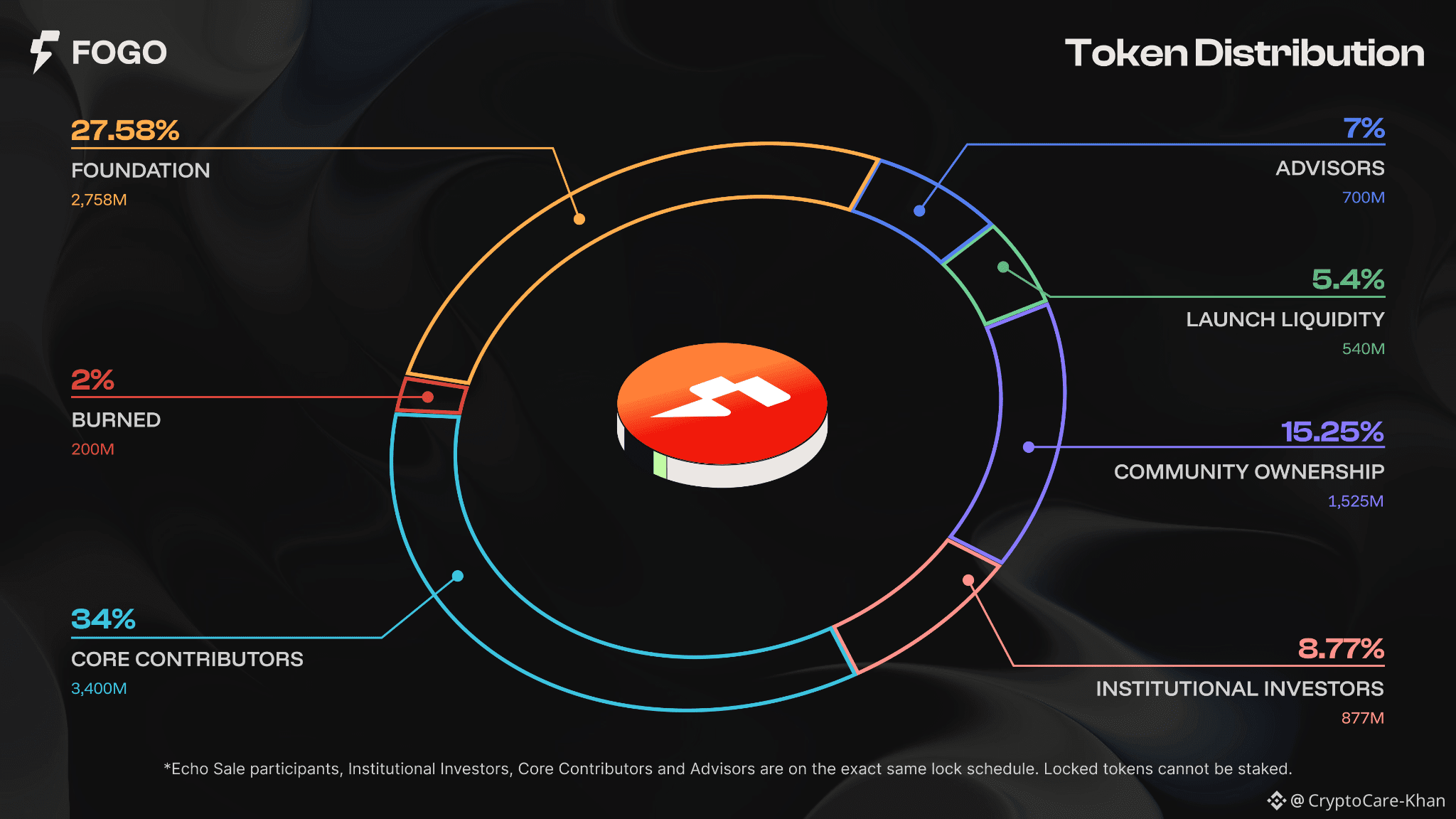
Unlike many general-purpose blockchains that attempt to support a wide range of use cases, Fogo chose a specialized direction. The network concentrates on ultra-low latency trading, derivatives markets, and financial applications that depend on real-time interaction. This focus influenced every technical decision made along the way.
Technically, Fogo is designed as more than a simple chain of blocks. It functions as a layered infrastructure system optimized for performance. The network operates using the Solana Virtual Machine, enabling parallel transaction execution and compatibility with established development tools. However, the team went further by redesigning key parts of the validator client and networking stack to minimize delay.
A major step involved integrating a high-performance validator implementation inspired by Firedancer. This approach targets significant increases in throughput while reducing latency, with block times around forty milliseconds. Such responsiveness transforms user interaction. Instead of waiting several seconds for confirmation, users receive feedback almost instantly, creating an experience closer to centralized trading systems.
The network also incorporates multi-local consensus with dynamic colocation. Validators remain geographically distributed but are strategically positioned to reduce communication lag during peak activity. If one cluster encounters issues, consensus shifts to maintain stability. This reflects an attempt to balance resilience and performance rather than prioritizing decentralization in its most absolute form.
Additionally, Fogo begins with a curated validator set. Rather than allowing unrestricted participation at launch, it limits validators to those meeting strict performance standards. While some critics argue this reduces decentralization, the team maintains that high-speed execution is necessary to attract adoption first. Broader validator expansion may follow as the ecosystem matures.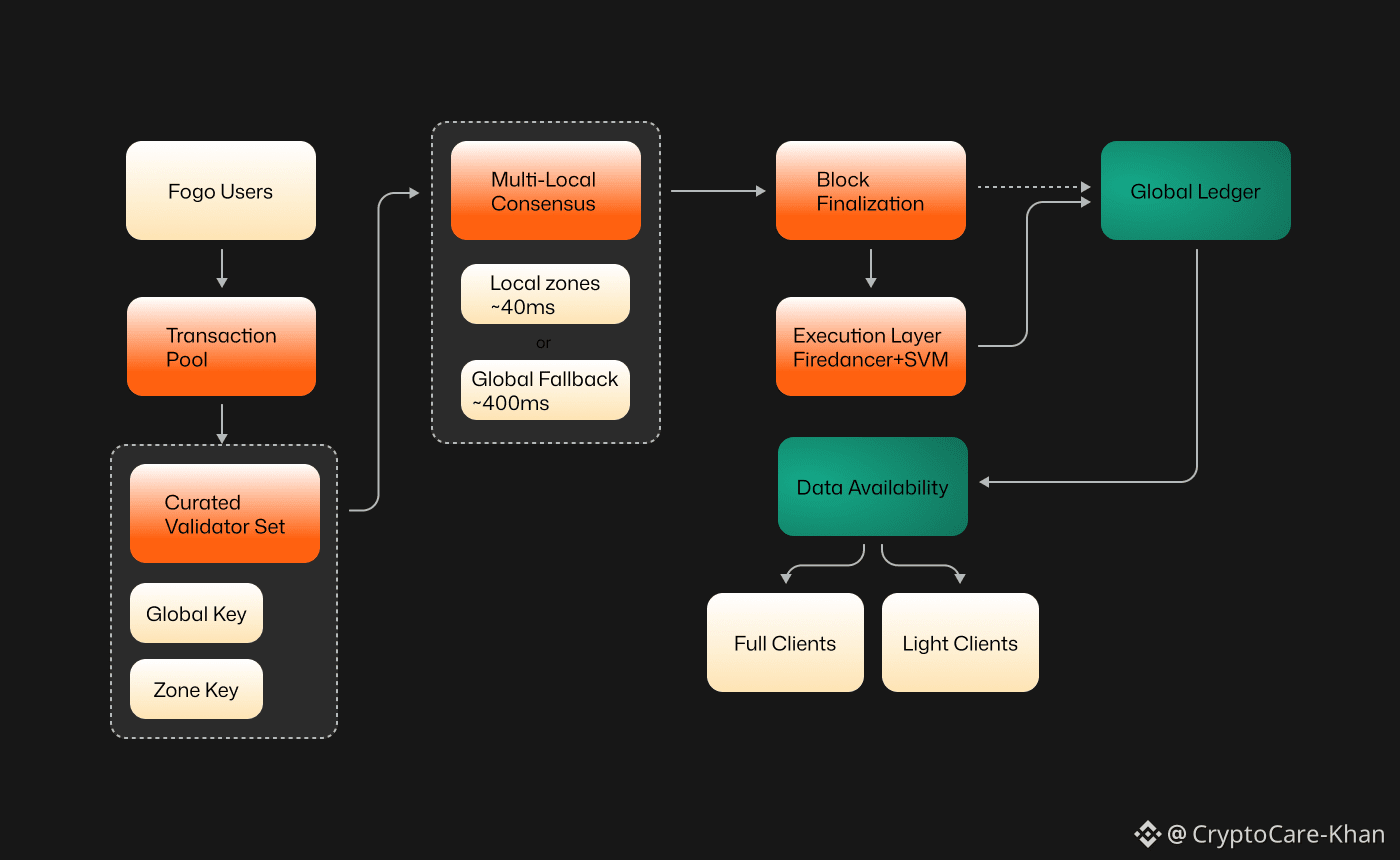
Beyond faster block production, Fogo integrates essential trading components directly into the protocol. Native price feeds, trading primitives, and colocated liquidity vaults are embedded within the network’s design. This vertically integrated structure reduces reliance on external services and off-chain infrastructure.
Parallel execution further enhances performance. Instead of processing transactions sequentially, the network handles multiple operations simultaneously, dramatically increasing throughput. In controlled test environments, performance has reportedly exceeded one hundred thousand transactions per second. These figures place Fogo among the fastest experimental Layer 1 networks currently under development.
User experience is another area of focus. Session-based account management enables streamlined or gasless interactions, reducing the need for repetitive signing. For active traders, this makes decentralized applications feel more like traditional web platforms.
Although transaction-per-second metrics often attract attention, long-term success depends on additional factors. Consistent block times, rapid finality, and stable latency matter more to traders than peak throughput under ideal conditions. With block generation targeted around forty milliseconds, confirmation windows shrink considerably compared to many existing networks. The architecture also includes measures aimed at reducing maximum extractable value and improving fairness in trading environments.
However, adoption will ultimately determine impact. Trading volume, ecosystem development, and institutional participation will reveal whether performance advantages translate into sustained relevance.
Fogo’s token design reflects its view that decentralization evolves over time. A significant portion of token supply remains locked at launch to align contributors and investors with long-term goals. Airdrops and public offerings are structured to distribute ownership broadly while maintaining development funding.
The funding strategy emphasizes community participation rather than heavy reliance on venture capital. Early fundraising involved widespread engagement, reinforcing the goal of cultivating a broad supporter base. Incentives are designed so that developers, traders, and long-term contributors all benefit from ecosystem growth.
Exchange listings, including Binance, increased liquidity and visibility but also introduced volatility typical of early-stage blockchain projects. The team has acknowledged that lasting token stability will depend on genuine ecosystem usage rather than short-term speculation.
The project’s performance-first philosophy does involve trade-offs. A limited validator set raises ongoing questions about decentralization. Critics caution that curated participation may introduce governance risks, particularly during rapid expansion. Maintaining low latency under real-world stress conditions is another uncertainty, as high throughput claims often rely on controlled testing environments. To address this, Fogo emphasizes phased deployment and permissioned testnets designed to rigorously evaluate infrastructure before broader release.
Security considerations accompany new consensus mechanisms and networking strategies. Geographic distribution of nodes provides redundancy, but long-term resilience will only be confirmed through sustained operation and real-world usage.
Within the broader blockchain landscape, Fogo represents a shift toward specialization. Rather than aiming to support every application type, it concentrates on trading and real-time financial use cases. This narrow focus allows deeper optimization but also defines a specific target audience.
Developers are experimenting with latency-sensitive applications such as real-time order books and automated liquidation systems. Institutional interest appears to be increasing, especially among those seeking infrastructure that mirrors the execution speed of traditional financial markets. Whether these performance advantages will translate into lasting ecosystem growth remains uncertain, as community engagement and developer participation ultimately determine success.
Looking ahead, Fogo’s roadmap frames decentralization as a gradual process. Early phases emphasize reliability and speed, while future stages may expand validator participation and governance mechanisms. If adoption grows, the network could enable decentralized financial applications operating at speeds once thought impossible on public blockchains.
At a deeper level, the project challenges rigid interpretations of decentralization. Rather than viewing it as a fixed condition, Fogo treats it as a spectrum that can evolve while still preserving openness and shared ownership.
The story of Fogo is still unfolding. Its long-term impact remains to be seen, but it represents a moment in blockchain development when builders refuse to accept a forced choice between speed and decentralization. If the approach succeeds, it could reshape expectations around what decentralized infrastructure can deliver. Ultimately, the project is not just about faster block times or higher transaction counts. It reflects the broader idea that decentralized systems can adapt, refine their architecture, and potentially transform how people experience financial markets.
