In the current Layer 1 environment, performance claims are everywhere. Speed metrics, throughput numbers, and scalability statements dominate headlines. But beneath those surface comparisons lies a deeper question: what kind of execution model is actually powering the network?
@Fogo Official approaches this from an architectural standpoint. Rather than focusing solely on performance statistics, it is built around the Solana Virtual Machine an execution framework known for enabling parallel transaction processing. That design choice influences how transactions are validated, how workloads are distributed and how efficiently the system handles simultaneous activity.
Execution architecture is more than a technical detail. It determines how applications behave under real demand. When usage increases, sequential bottlenecks can expose limitations in weaker systems. Parallel execution environments aim to reduce that friction by allowing compatible transactions to process simultaneously instead of waiting in line.
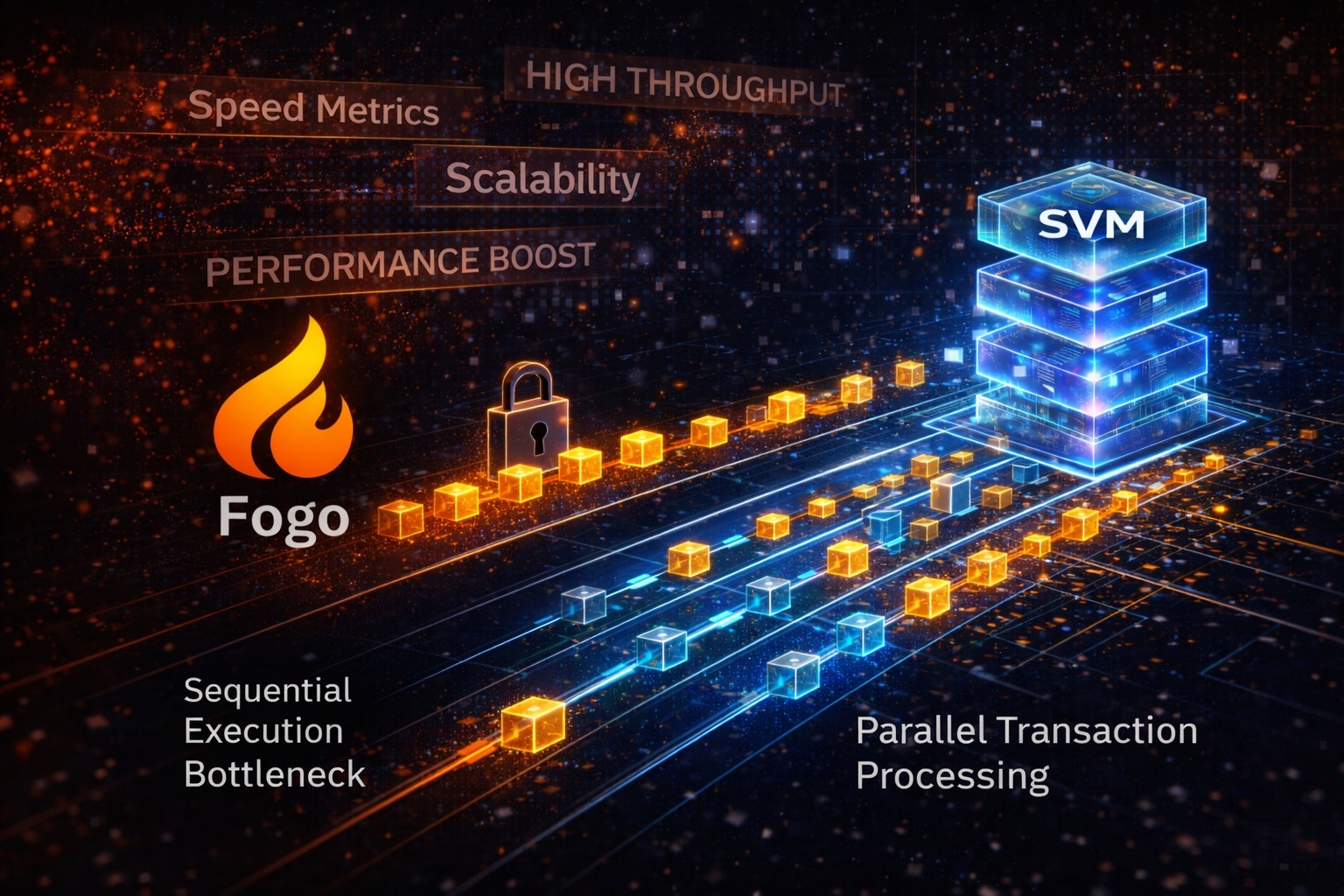
For developers, this creates flexibility. Applications that require responsiveness whether they involve complex logic or frequent state updates depend on predictable performance at the base layer.. Infrastructure that scales with activity becomes an enabler rather than a constraint.
As the market matures, evaluation standards are rising. Builders and observers increasingly look at execution frameworks, system structure and deployment capacity instead of relying purely on marketing positioning. Strong infrastructure doesn’t automatically create adoption but weak infrastructure often restricts it.
Fogo’s high-performance positioning reflects this architectural priority. By leveraging the Solana Virtual Machine, it aligns its foundation with an execution model designed for efficiency and scalable deployment. #fogo

In a competitive Layer 1 landscape, foundational design choices may ultimately determine which networks sustain growth — and which struggle when real usage begins.

