introduction
The crypto world is growing faster than ever, but with that growth comes a massive challenge:
👉 Blockchains can’t handle millions of users at once.
Transactions get slow. Fees get expensive. Networks get congested.
This challenge is exactly why the terms Layer 1 and Layer 2 exist.
If you’ve ever wondered…
What exactly makes a blockchain “Layer 1”?
Why Layer 2 networks like Polygon or Arbitrum are exploding in popularity?
Whether Layer 2 will replace Layer 1 in the future?
…then this blog breaks everything down in simple, human language.
Let’s dive in.
What Is Layer 1? (The Base Blockchain Layer)
Layer 1 is the foundation of a blockchain ecosystem.
It is the main network where transactions are recorded, validated, and secured.
Examples of Layer 1 blockchains:
Bitcoin
Ethereum
Solana
BNB Chain
Avalanche
Cardano
These networks are responsible for:
✔ Security
✔ Consensus (PoW, PoS, etc.)
✔ Storing data
✔ Executing smart contracts (for chains like Ethereum and Solana)
The Problem with Layer 1
As more people use a blockchain:
❌ It becomes slower
❌ Transaction fees increase
❌ Processing capacity hits limits
This is known as the blockchain scalability problem.
Popular Layer 1 Blockchains Explained
1. Bitcoin (BTC)
The most secure blockchain
Designed for peer-to-peer money
Very decentralized
But slow (only ~7 transactions per second)
2. Ethereum (ETH)
The world’s largest smart-contract platform
Hosts DeFi, NFTs, and dApps
But during congestion, gas fees can skyrocket
3. Solana (SOL)
Extremely fast (65,000+ TPS)
Popular for gaming, memecoins, DeFi
But has faced network outages
4. BNB Chain
Fast and affordable
Widely used for trading and new tokens
What Is Layer 2? (The Scaling Layer on Top of Layer 1)
Layer 2 blockchains are secondary networks built on top of Layer 1 to improve speed and reduce fees.
Layer 2s don’t replace the main blockchain — they assist it.
Examples:
Polygon (Matic)
Arbitrum
Optimism
Base
Lightning Network (for Bitcoin)
These networks handle large batches of transactions off-chain and then settle them on Layer 1 for security.
This gives users:
✔ Faster transactions
✔ Ultra-low fees
✔ Higher throughput
✔ Better user experience
Types of Layer 2 Solutions
1. Rollups (Most Advanced)
Rollups “roll up” thousands of transactions and submit them to Ethereum.
Two main types:
• Optimistic Rollups – Arbitrum, Optimism
• ZK-Rollups – zkSync, StarkNet, Polygon zkEVM
2. State Channels
Parties transact privately and only record the final result on-chain.
Example: Bitcoin Lightning Network.
3. Plasma Chains
Child chains that handle transactions separately.
4. Sidechains
Independent blockchains connected to Layer 1, but not true L2.
Example: Polygon PoS.
Layer 1 vs Layer 2: Key Differences
FeatureLayer 1Layer 2PurposeBase blockchainScaling solutionSpeedSlowerFasterFeesHigherVery lowSecurityHighestInherits security from L1ExamplesBTC, ETH, SOLPolygon, Arbitrum, Optimism
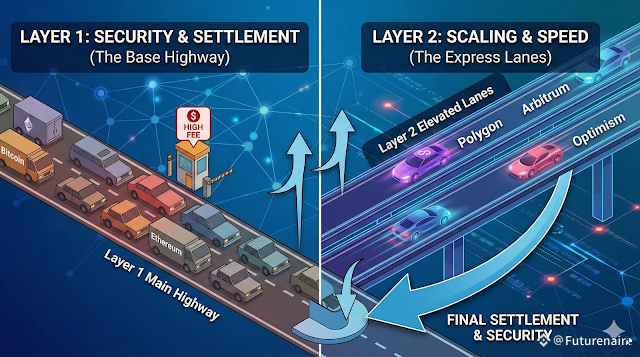
How Layer 1 and Layer 2 Work Together
Think of it like a highway:
Layer 1 = the main highway
Layer 2 = extra lanes built above it
Layer 1 provides security, while Layer 2 provides scalability.
They are not competitors — they are complementary.
Real-World Use Cases for Layer 2
1. Payments
Instant crypto payments using Polygon or Lightning Network.
2. NFTs
Minting costs drop from $30 to under $0.01 on L2.
3. DeFi
Layer 2 enables cheaper swaps, borrowing, and staking.
4. Gaming
High-speed transactions needed for Web3 games.
5. Microtransactions
Small payments (like $0.10) become possible.
Why Layer 2 Is Essential for Crypto Adoption
For crypto to reach billions of users, we need:
fast networks
cheap transactions
high scalability
better UX
Layer 2 solves all of these challenges without sacrificing Layer 1 security.
Will Layer 2 Replace Layer 1?
Short answer: No.
Layer 2 depends on Layer 1 for settlement and security.
Layer 1 is the “source of truth,” while Layer 2 is the “performance upgrade.”
Both will coexist.
Think of it like this:
Layer 1 = the judge
Layer 2 = the assistants who process paperwork faster
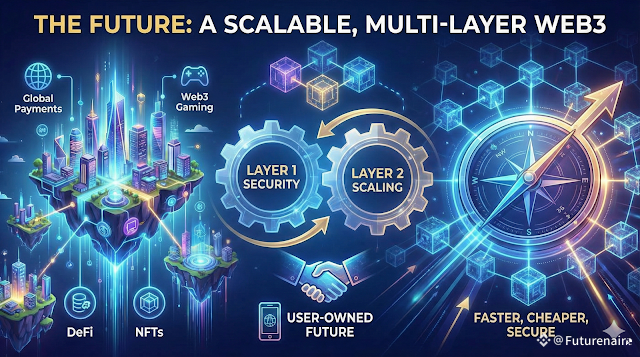
The Future of Blockchain: Multi-Layer Ecosystems
The future will have:
Many Layer 2 networks
Faster Layer 1 upgrades
Cross-chain bridges
Big companies building on Layer 2 (Coinbase → Base blockchain)
Ethereum’s upcoming upgrades (Danksharding) will make Layer 2s even more powerful.
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is already growing for global payments.
Conclusion: Why This Matters for You
Understanding the difference between Layer 1 and Layer 2 helps you:
✔ avoid confusion
✔ choose the right networks for investing
✔ save money on fees
✔ understand where crypto is heading
Layer 1 gives us security.
Layer 2 gives us speed and affordability.
Together, they build a scalable, fast, and user-owned Web3 future.