Dusk Network brands itself as a privacy blockchain for financial applications. It is a layer-1 blockchain that powers the Confidential Security Contract standard, and supports confidential smart contracts. Dusk Network aims to address the requirements and needs of financial markets. Central to its design are thus a scalable public infrastructure, direct settlement finality of transactions, and strict data privacy.
Through the use of a novel transactional model called Phoenix, Dusk Network focuses to bring privacy and anonymity to transactions, as well as smart-contracts. Additionally, tokens deployed on Dusk Network can build on top of Zedger, a hybrid privacy-preserving model based on Phoenix, developed specifically for security tokens.
The ‘Segregated Byzantine Agreement consensus mechanism secures the network. According to the team from Dusk Network, SBA is an improvement over the underlying Proof-of-Stake mechanism as it combines existing ideas like "cryptographic sortition stealth time-locked transactions (hidden stake amounts) and a reputation module to increase the chances of selecting honest nodes and further promote decentralization".
DUSK tokens can be used as a utility token to initiate transactions, atomic swaps or deploy smart contracts. DUSK can also be staked to participate in consensus and serves as a means of exchanging DUSK-denominated value. In the future, the team intends to expand the use-cases of DUSK by adding it to an on-chain governance system.
What is Dusk Network
Dusk Network is a privacy-oriented blockchain protocol featuring Segregated Byzantine Agreement to provide privacy, programmability, and contract auditability.
Dusk is built by a team of entrepreneurs, engineers and researchers with technical experience at Amazon, TomTom, Mozilla, Reaktor, and blockchain backgrounds.
Dusk Network is currently in testnet phase and aims to be a blockchain protocol designed for easy deployment of programmable Zero Knowledge dApps, thus becoming the backbone of an open, permissionless and global privacy-oriented dApp ecosystem.
The Project aims to remove technical barriers that have hindered mainstream issuance and trading of products such as security tokens. Compliance, auditability and privacy are built into the open, permissionless Confidential Security Token Standard.
Some of its key elements include:
Raised ~$8.08MM via private token sales from August to November 2018
Private Proof-of-Stake implementation which enables Block Generators to stake anonymously.
Utilizes ZeroCaf to achieve fast, efficient and Bulletproof-friendly Elliptic Curve operations.
Built by a team of entrepreneurs, engineers, and researchers from a wide variety of backgrounds.
Dusk Network aims to achieve on-chain privacy and programmability while maintaining high-throughput and instant transaction finality. Dusk Network is built upon these key innovations:
Some of its key features include
Private-Proof-of-Stake: Dusk Network's consensus protocol, Segregated Byzantine Agreement is powered by "Proof of Blind Bid" that enables Block Generators to stake anonymously.
Decentralization: by disincentivizing resource centralization from staking pools, smaller participants are encouraged to partake in the consensus.
Replaceability: consensus participants are chosen pseudo-randomly and independent of earlier outcomes.
To do so, Dusk relies on a few core characteristics:
Consensus in three phases: Block Generation, Block Reduction and Block Agreement.
ZeroCaf for fast, efficient and Bulletproof-friendly Elliptic Curve operations. ZeroCaf is an Elliptic Curve developed on the Ristretto scalar field.
Implementation of Poseidon, a Zero-Knowledge friendly hashing algorithm.
Browser Nodes for Zero-Knowledge verification and Zero-Knowledge Virtual Machine architecture.
Instant Transaction Finality: Due to the properties of the Dusk Network consensus protocol transactions are final immediately after the completion of a block, aside from a negligible probability of a fork.
Mission and value proposition
By allowing Dusk to be openly accessible, Dusk Networks's mission is to become "the privacy infrastructure of choice for an entire ecosystem of solutions, whether in finance, governance, cybersecurity, or something completely new".
With a combination of privacy and compliance, Dusk is designed for the financial industry use, and as such, Dusk's adoption strategy focuses on the security token market, which is in need of a purpose-built blockchain.
Privacy: Dusk Network provides speed and full user privacy, while enabling decentralized application issuers and third-parties to create meaningful Zero Knowledge proofs to fulfill checks and balances, and audit & reporting requirements.
Permissionless: anybody can join the network as a consensus participant without a need for approval from a central entity.
Public: users do not need approval of a trusted authority to use the Dusk Network blockchain. The Dusk Network blockchain also requires minimal processing power and modest IT resources to join. All users who possess the DUSK token can participate in the consensus.
Compliance: through zero-Knowledge proofs, companies and projects are able to create real world applications that can adhere to strict compliance requirements whilst still offering data privacy. This increases the ability to perform business processes on-chain, leading to significant cost reduction.
Dusk Network uses zero-knowledge cryptography to allow network participants to prove the correct outcome of a wide range of operations without revealing identities or any transaction details while provide proof of correct computation in a trustless manner. The browser nodes are used to provide these different types of verification.
Dusk nodes compete in the block selection process by anonymously committing staking an undisclosed amount of Dusk tokens and thus prove compliance to the process by generating a Zero Knowledge proof of such transaction. By delegating to the browser the workload of verifying (or even generate) Zero Knowledge proofs, they can leverage game theoretic principles to let the community help with the computation power required to verify Zero Knowledge proofs multiple times and bring Dusk Network one step closer to a fully browser based blockchain experience.
DUSK token overview and use-cases
The DUSK token is used to stake and participate in the consensus.
DUSK token is used to pay for transactions deploying dApps, and as gas. The token also serves as rewards for the consensus participants.
DUSK can be traded for XSC-based tokens, both one-way and through atomic swaps.
The DUSK token will be used for on-chain governance within XSC once it is released.
In Dusk Network, block rewards are paid through an emission of DUSK defined in the protocol. The majority of all newly issued DUSK will be rewarded to consensus participants, while a minor portion will go to a technical development fund, creating an autonomous funding mechanism for the long term research and development
Key products and features
Segregated Byzantine Agreement
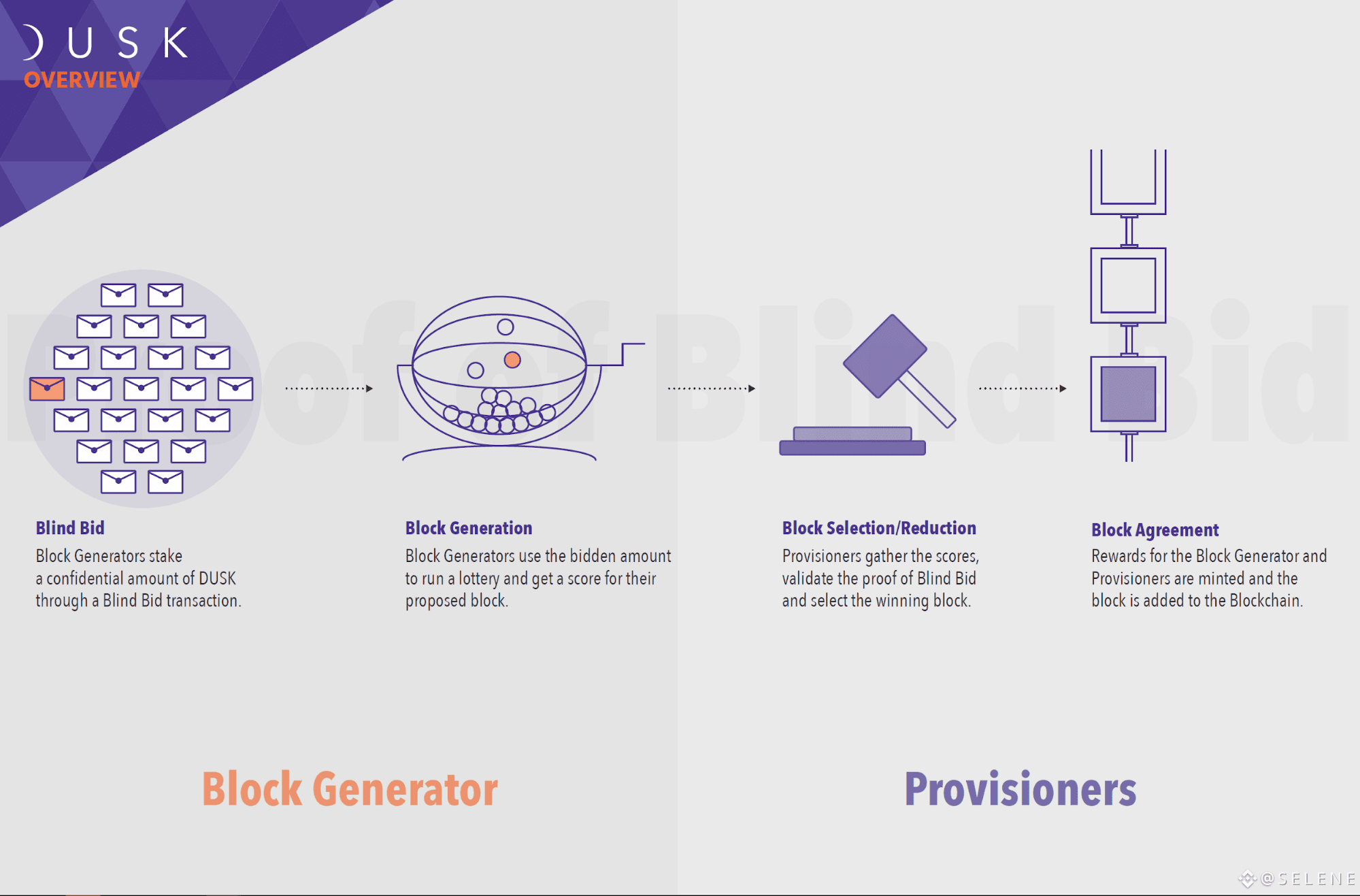
The roles in the protocol are split between two different node types: Block Generators and Provisioners.
Block Generators compete in a recurring lottery for the right to submit block candidates, while Provisioners run consensus over the selection of the lottery winners and acceptance of their proposed block.
In order to become Block Generators, full nodes submit a confidential transaction called Blind Bid. Provisioners, instead, are required to stake their DUSK publicly, while participating in the consensus
A unique consensus mechanism
Blind Bid Phase
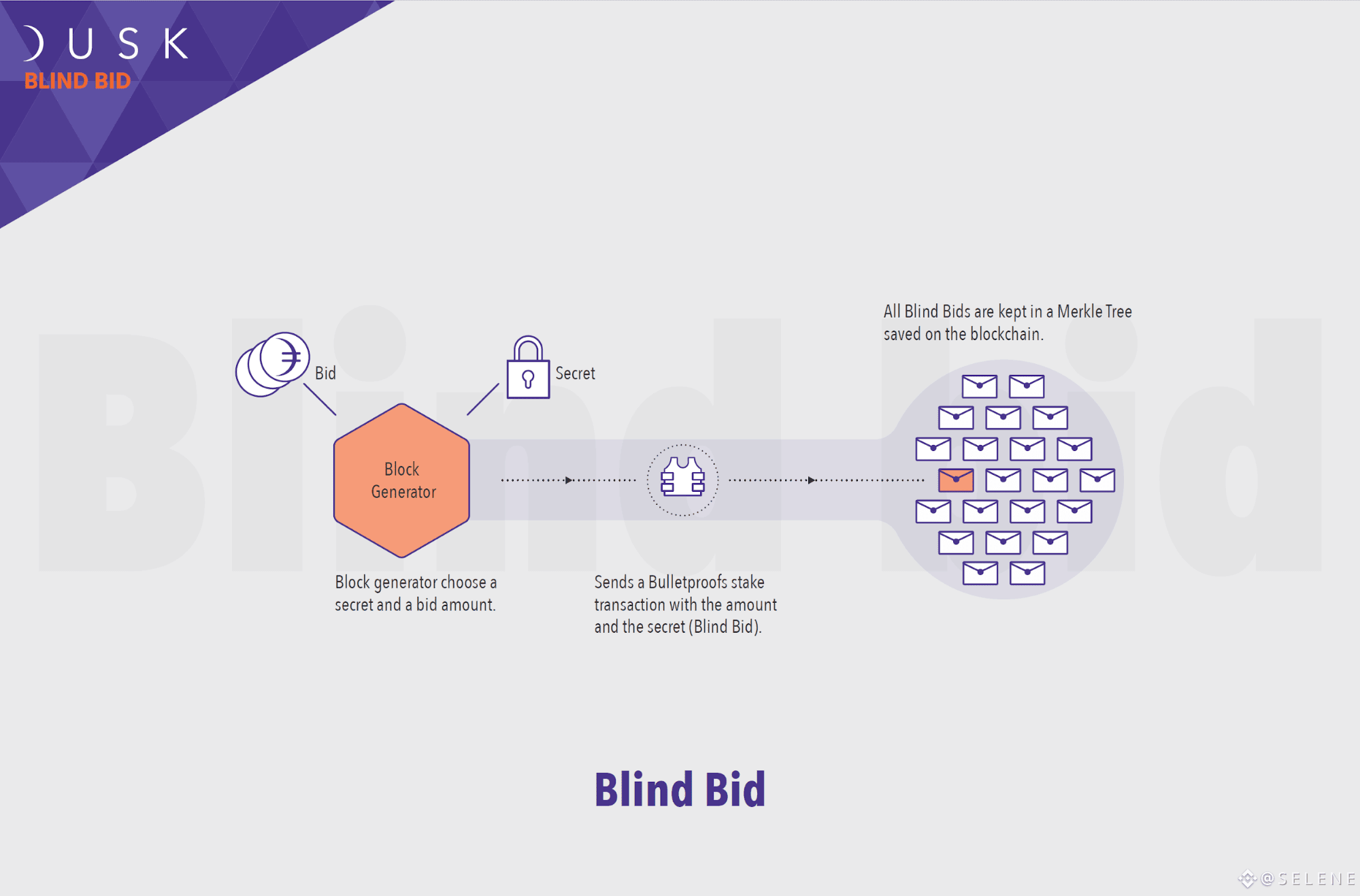
During the Blind Bid phase, aspiring Block Generators stake an amount of DUSK for the right to participate in the block generation lottery. The stake transaction is called a Blind Bid, because the amount of DUSK staked and the identity of the Block Generator are kept confidential. The Blind Bid also carries a secret number 'k' chosen arbitrarily by the Block Generator. This way she can claim ownership of her own transaction at any time, despite its confidentiality and without disclosing her identity. All valid Blind Bids are kept in a Merkle Tree saved on the blockchain.
Consensus Phase - Block Generation and Selection
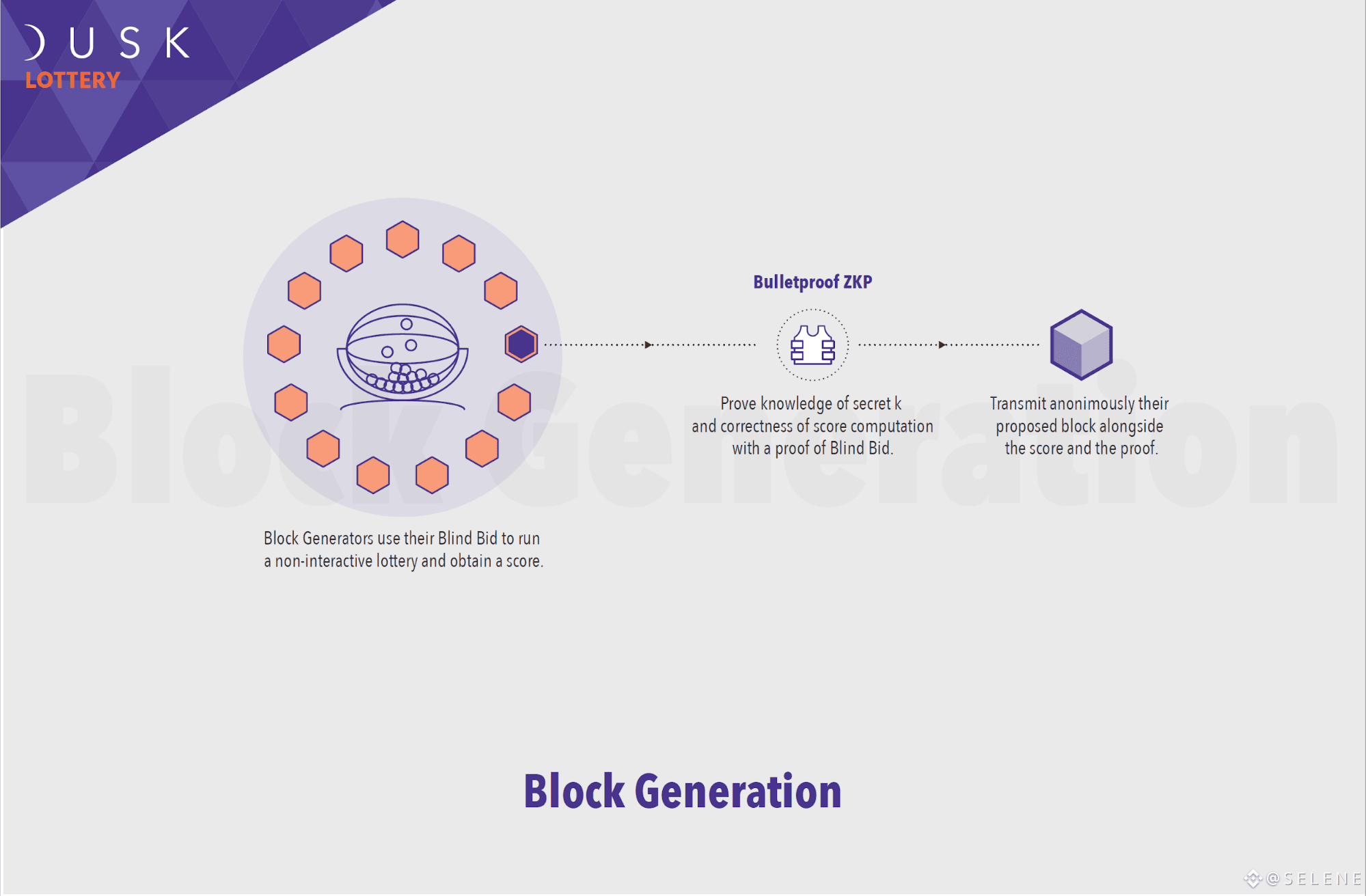
During each round, Block Generators use their Blind Bid to run a non-interactive lottery and obtain a score.
The amount of DUSK in the Blind Bid positively affects this score.
Thus, Block Generators anonymously transmit their proposed block to the Provisioners alongside the obtained score and the Zero Knowledge proof of Blind Bid; therefore proving knowledge of the embedded secret 'k' and the correctness of the score computation. Due to the reliance upon Zero Knowledge proof of correctness, proof of Blind Bid provides a significantly higher level of security if compared to public Proof-of-Stake systems while showing an equal resilience to Sybil attacks.
A committee of Provisioners validates all submissions and select the candidate block with the highest score.
Consensus Phase - Block Reduction
After the Selection phase, a small committee of Provisioners perform Block Reduction: a two step routine to gather Provisioners' signatures and assure convergence over a single block. If more signatures than a threshold of 75% of committee participants are collected, the candidate block is then established. The committee chosen for Block Reduction is always a small subset of the entire provisioner population, deterministically extracted through a non-interactive algorithm called "deterministic sortition". The non-interactive deterministic extraction algorithm additionally enables every node in the network to calculate who is in the committee from public parameters. This can be used to single out compromised participating Provisioners and decrease their reputation.
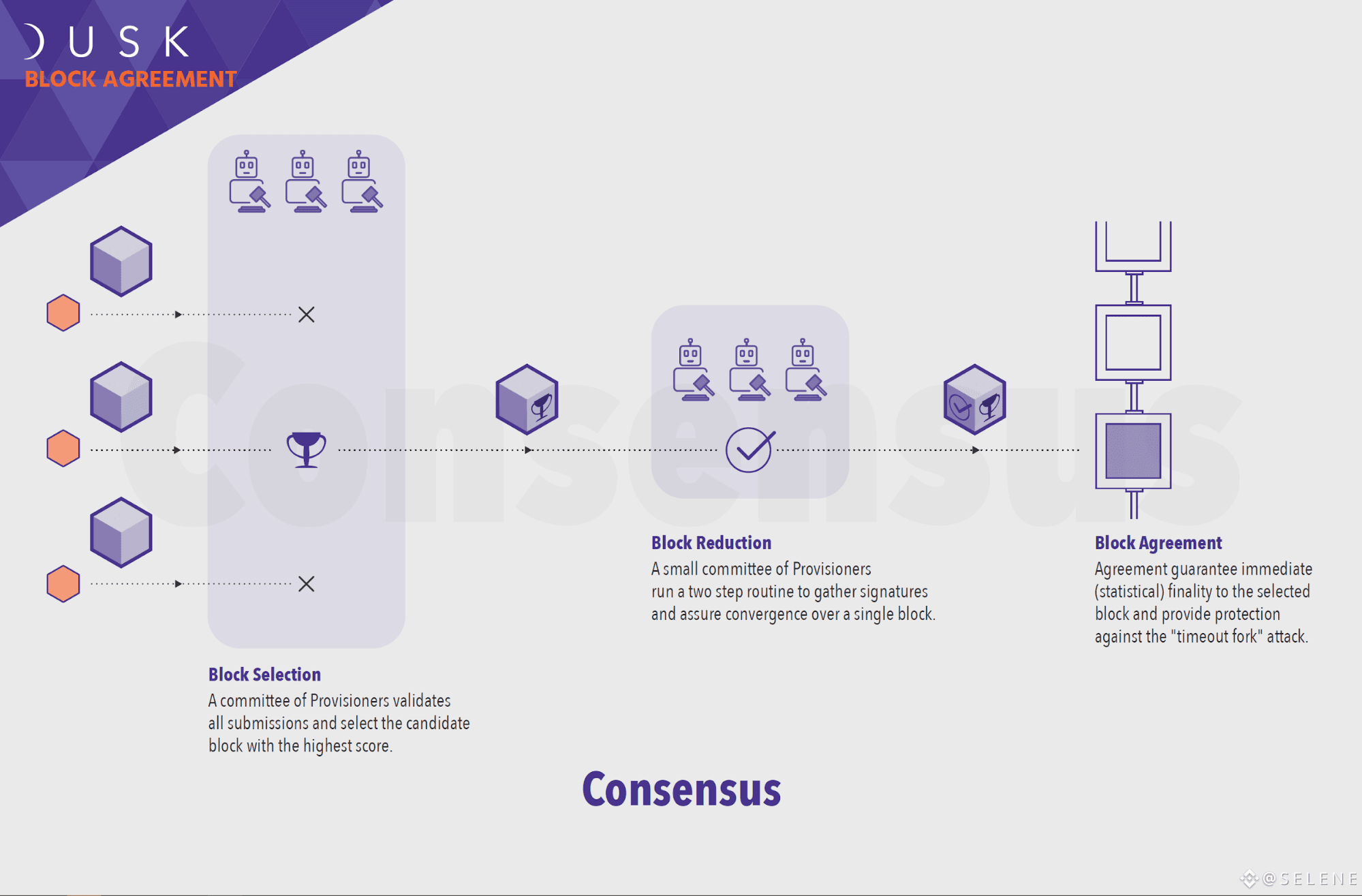
The Block Agreement is an additional phase designed to guarantee immediate finality to the selected block and provide protection against the "timeout fork" attack. During this phase, an additional committee gathers and verifies the signatures collected at the Reduction phase. This phase provides a statistical guarantee that at least one honest node has received a set of votes exceeding the minimum threshold required to successfully terminate the respective phase of the protocol.
If the candidate block does not reach sufficient signatures, or agreement votes, the candidate block is omitted from the pool of candidate blocks and the process loops back to the selection stage. This time another candidate block with the highest score is selected and the process repeats until a favorable outcome is reached.
