The global financial system is undergoing one of the most profound transformations in modern history. At the heart of this shift lies blockchain technology—particularly Layer 1 blockchains, the foundational networks that power decentralized applications, digital assets, and borderless financial services. As scalability improves, transaction costs fall, and real-world adoption grows, Layer 1 blockchains are redefining how value moves across the world.
Projects such as @undefined are pushing this evolution forward by developing high-performance Layer 1 infrastructure designed for mass adoption, gaming, digital entertainment, and decentralized finance. The rise of innovative networks and utility-driven tokens like VANRY reflects a broader trend: Layer 1 blockchains are no longer experimental—they are becoming core pillars of tomorrow’s financial architecture.
This article explores how Layer 1 blockchains are reshaping financial markets, enabling new economic models, and opening unprecedented opportunities for individuals, institutions, and underserved populations worldwide.
Understanding Layer 1 Blockchains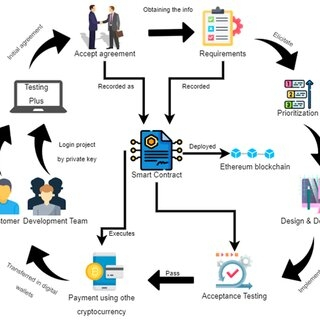
A Layer 1 blockchain is a base-layer network that processes and finalizes transactions independently. Unlike Layer 2 solutions, which operate on top of existing blockchains, Layer 1 chains maintain their own consensus mechanisms, validators, and security models.
Popular examples include:
Bitcoin (BTC)
Ethereum (ETH)
Solana (SOL)
Avalanche (AVAX)
Polkadot (DOT)
Vanar Chain
Each of these networks offers unique trade-offs between decentralization, security, and scalability. However, modern Layer 1 projects are increasingly focused on solving the “blockchain trilemma” — achieving all three simultaneously.
Why Layer 1 Blockchains Matter for Financial Markets
Traditional financial infrastructure relies on centralized intermediaries such as banks, clearing houses, and payment processors. These systems are often slow, costly, and inaccessible to billions of people worldwide.
Layer 1 blockchains introduce a radically different model:
Permissionless access
24/7 settlement
Near-instant finality
Lower transaction costs
Global reach
These features enable financial activity to occur directly between participants without relying on centralized gatekeepers.
Scalability: Powering High-Volume Financial Activity
One of the biggest challenges early blockchains faced was scalability. Congestion and high fees limited adoption. Today’s advanced Layer 1 networks use innovative techniques such as:
Sharding
Parallel execution
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus
Optimized virtual machines
Vanar Chain is designed with scalability at its core, making it well-suited for high-throughput use cases like gaming economies, NFT marketplaces, and microtransactions—areas that require thousands of transactions per second.
As scalable Layer 1s mature, they can support:
High-frequency trading platforms
On-chain derivatives markets
Payment rails for global commerce
This brings blockchain technology closer to matching — and eventually surpassing — traditional financial infrastructure.
Decentralization: Reducing Systemic Risk
Centralized financial institutions concentrate risk. History has shown that failures at major institutions can cascade across entire economies.
Layer 1 blockchains distribute trust across thousands of nodes, creating:
Censorship resistance
Fault tolerance
Increased transparency
Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols built on Layer 1 networks allow users to lend, borrow, trade, and earn yield without relying on banks. Smart contracts enforce rules automatically, reducing counterparty risk.
Vanar’s ecosystem is exploring decentralized applications that blend entertainment, gaming, and finance—unlocking new digital economies powered by user-owned assets.
Security: Cryptographic Trust at Scale
Layer 1 blockchains rely on cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms that make tampering extremely difficult. Security is enhanced through:
Validator incentives
Slashing mechanisms
Transparent ledgers
Open-source code
Institutional investors increasingly view major Layer 1 networks as robust settlement layers capable of handling large volumes of value securely.
As security frameworks continue to evolve, blockchain networks are becoming viable alternatives to traditional clearing and settlement systems.
Tokenization of Real-World Assets
One of the most promising applications of Layer 1 blockchains is asset tokenization—the process of representing real-world assets on-chain.
Examples include:
Real estate
Commodities
Stocks and bonds
Art and collectibles
Intellectual property
Tokenization enables:
Fractional ownership
Increased liquidity
24/7 trading
Global investor access
Layer 1 networks provide the base infrastructure required for secure issuance, custody, and transfer of tokenized assets.
Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
Sending money internationally is often expensive and slow. Fees can exceed 10%, and settlement may take days.
Layer 1 blockchains enable:
Near-instant transfers
Minimal fees
No intermediary banks
For migrant workers and underserved populations, this represents a massive improvement. Families can receive funds faster, and small businesses can participate in global trade more easily.
Vanar Chain’s focus on low-cost, high-speed transactions positions it as a strong candidate for powering next-generation payment solutions.
Financial Inclusion for the Unbanked
Over 1.4 billion people worldwide remain unbanked. Layer 1 blockchains require only:
A smartphone
An internet connection
A digital wallet
This opens access to savings, lending, insurance, and investment opportunities previously unavailable to large segments of the population.
Blockchain-based identity solutions, stablecoins, and decentralized lending platforms are helping bridge this gap.
Challenges Facing Layer 1 Blockchains
Despite their promise, Layer 1 networks face several challenges:
1. Scalability vs. Decentralization
Some networks sacrifice decentralization to achieve higher throughput.
Solution: Modular architectures and improved consensus designs.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments worldwide are still defining how blockchain fits into existing frameworks.
Solution: Clear compliance tools, transparency, and collaboration with regulators.
3. User Experience
Wallet complexity and key management can be intimidating.
Solution: Account abstraction, social recovery, and simplified interfaces.
Projects like @Vanar are actively building user-friendly infrastructure to drive mainstream adoption.
Institutional Adoption and Capital Inflows
Major financial institutions are now:
Launching crypto funds
Exploring tokenized securities
Using blockchain for settlement
Layer 1 blockchains serve as the backbone for these initiatives. As confidence grows, billions of dollars in institutional capital are expected to flow into the space.
Utility-focused tokens such as VANRY stand to benefit from increased ecosystem usage and long-term network growth.
The Long-Term Impact on Global Finance
Over the next decade, Layer 1 blockchains may:
Replace legacy settlement systems
Power decentralized capital markets
Enable programmable money
Create new digital economies
Rather than eliminating traditional finance, blockchain will integrate with it—creating hybrid systems that combine efficiency, transparency, and security.
Conclusion
Layer 1 blockchains represent the foundation of a new financial era. By enabling decentralized, scalable, and secure networks, they are transforming how value is created, transferred, and stored.
With innovative projects like @undefined leading the way, and growing adoption of tokens like VANRY, the future of finance is becoming increasingly open, inclusive, and programmable.
As institutional investment accelerates and real-world use cases expand, Layer 1 blockchains are positioned to reshape the global financial ecosystem for generations to come.

