
When people talk about blockchain adoption, they usually focus on speed, fees, or decentralization. Those things matter, but none of them solve the problem that has quietly blocked real finance from coming onchain for more than a decade. Markets do not collapse because transactions are slow. They collapse because trust fails. Orders are leaked. Front-running happens. Settlement is disputed. Compliance cannot be proven. And regulators, when they cannot see, assume the worst.
This is the invisible wall that separates crypto from capital markets.
Dusk’s Trust Stack exists because of that wall. It is not a privacy layer added to DeFi. It is not a zk rollup. It is not a compliance tool bolted onto a public chain. It is a purpose-built financial trust architecture designed to let regulated assets live onchain without breaking the rules that make markets function.
What makes @Dusk different is that it does not try to replace financial systems. It recreates their trust primitives using cryptography instead of intermediaries.
To understand why that matters, let’s understand how real markets actually work.
In traditional finance, trading is not just matching buyers and sellers. It is a choreography of confidentiality, fairness, auditability, and legal enforceability. Orders must be hidden until execution. Trades must be final. Positions must be verifiable. Regulators must be able to reconstruct what happened after the fact. None of this can be optional.
Public blockchains break almost every one of these requirements.
Every order is visible. Every wallet can be traced. Every trade exposes strategy. There is no way to selectively reveal information to regulators without revealing it to everyone else. And because of that, professional traders, market makers, asset issuers, and compliance teams simply cannot use them.
Dusk’s Trust Stack was designed from the ground up to solve this.
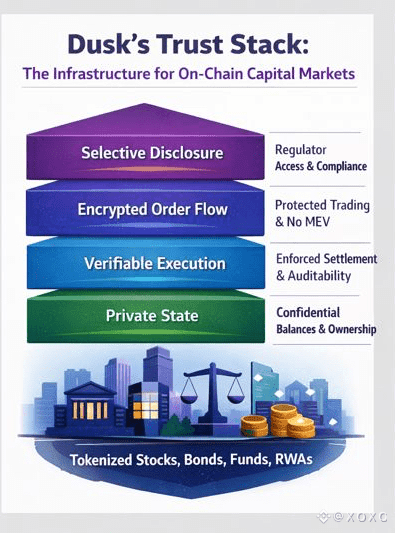
At its core, the Trust Stack is a layered architecture that allows private financial activity to happen on a public, verifiable ledger. It does this through four interlocking components: private state, verifiable execution, encrypted order flow, and selective disclosure.
Each layer replaces something that banks and exchanges used to do.
The first layer is private state. On Dusk, balances, positions, and ownership of regulated tokens are not public. They are stored in encrypted form, protected by zero-knowledge proofs. This means a trader can hold tokenized stocks, bonds, or funds without revealing their portfolio to the world.
This is not a cosmetic feature. It is foundational. In traditional finance, portfolio privacy is what prevents predatory trading. If competitors can see your positions, they can move against you. In crypto, this happens constantly. On Dusk, it does not.
The second layer is verifiable execution. Every trade, even though it is private, is still mathematically proven to follow the rules of the market. Order matching, settlement, margin requirements, and asset transfers all happen inside zero-knowledge circuits. The network does not see the trade details, but it can verify that the trade was valid.
This is the cryptographic equivalent of an exchange’s internal matching engine and clearinghouse.
The third layer is encrypted order flow. On DuskTrade, orders are not broadcast to the mempool. They are submitted in encrypted form. Market makers cannot see incoming trades. Bots cannot front-run. There is no MEV. What exists instead is a private auction where all participants are treated fairly.
This changes market structure in a profound way. Liquidity providers can quote tighter spreads because they are not being exploited. Institutions can trade size without being hunted. Retail traders are no longer the exit liquidity for invisible actors.
The fourth layer is selective disclosure. This is the bridge to regulation. On Dusk, every account and every asset can be associated with a compliance identity. Regulators, issuers, and auditors can be granted the ability to view specific transaction histories without exposing them publicly.
This means a tokenized share of a company can trade privately onchain, but the issuer and the regulator can still verify ownership, transfers, and compliance with securities law.
That combination is something no other blockchain offers.
When you put these layers together, you get something that looks less like DeFi and more like a digital stock exchange that happens to run on cryptography instead of servers.
This is why Dusk is not competing with Ethereum or Solana. It is competing with NASDAQ, DTCC, and the infrastructure behind capital markets.
The Trust Stack is what allows that.
It enables tokenized equities, funds, debt instruments, and real-world assets to exist as cryptographic objects without losing the legal and operational properties that make them investable.
Issuers can control who holds their assets. Regulators can audit flows. Traders can execute strategies without being exposed. And the network can still guarantee settlement finality.
This is what people mean when they talk about “institutional crypto.” Not ETFs. Not custodians. Actual on-chain capital markets.
Without a trust stack, tokenization is just a gimmick. With it, it becomes infrastructure.
And this is why Dusk’s approach matters far beyond its own ecosystem.
As more real-world assets move onchain, the question is not whether blockchains can handle the volume. It is whether they can handle the responsibility.
Dusk’s Trust Stack is built to answer that question with mathematics instead of promises.
My take
Most people think regulation and decentralization are opposites. Dusk proves they are complements. When trust is enforced by cryptography instead of institutions, you get markets that are fairer, safer, and more open. That is not the end of crypto’s vision. It is its first real beginning.