(Yield curve inversion)
This creates a 2Y > 30Y inversion, which screams:
"Recession risk ahead"
"Fed is too tight"
"Growth outlook is weak"
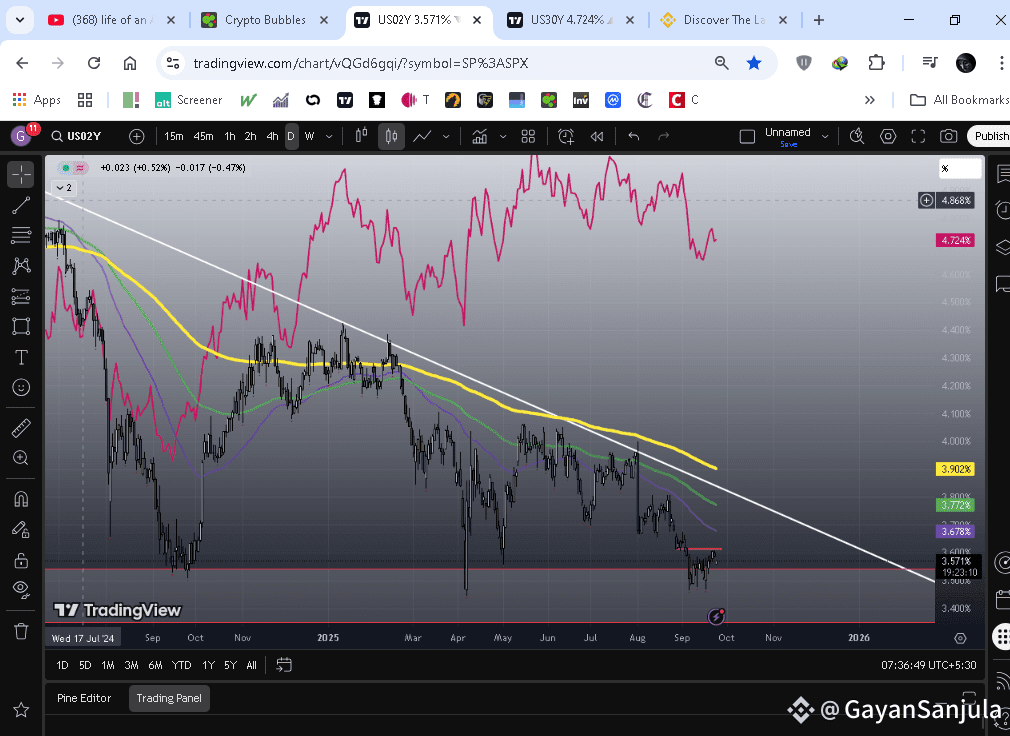
When the 2-Year Yield Rises and the 30-Year Yield Falls: What It Means for Crypto
The U.S. Treasury market is one of the most important indicators for global finance. Two of the most watched benchmarks are the 2-Year Treasury Note yield (UST2Y) and the 30-Year Treasury Bond yield (UST30Y). When these two yields move in opposite directions — the 2-year going up while the 30-year goes down — it sends a powerful signal about the economy and risk assets, including cryptocurrency.
🔹 What’s Happening?
2-Year Yield Rising:
A rising 2Y yield shows that markets expect the Federal Reserve to keep interest rates high in the near term. This reflects tighter monetary policy and stronger inflation concerns.30-Year Yield Falling:
A falling 30Y yield means investors are piling into long-term bonds, expecting slower growth, weaker inflation, or even a recession in the future. It signals demand for long-term safety.
🔹 Yield Curve Inversion
When the 2Y yield climbs above the 30Y yield, it creates a yield curve inversion. Historically, this is one of the most reliable warning signs of an upcoming recession. Investors believe the short-term outlook is risky and that long-term rates cannot stay high.
🔹 Why It Matters for Crypto
Short-Term Pressure (Bearish):
Rising short-term yields = tighter liquidity.
Cash and bonds become more attractive than risky assets.
Bitcoin and crypto often see selling pressure as money flows into safe, interest-bearing assets.
Long-Term Opportunity (Bullish):
Falling long-term yields = markets expect Fed rate cuts later.
Once the Fed pivots, liquidity returns and risk assets (stocks, crypto) tend to recover strongly.
Historically, major crypto bull runs have started after the Fed shifts from tightening to easing.
🔹 Example from History
2006–2007: Yield curve inverted → recession followed in 2008. Risk assets sold off, but liquidity injections later helped Bitcoin (launched in 2009) thrive in the easy money environment.
2019: Yield curve inverted → Fed pivoted and cut rates → Bitcoin rallied from $3k to $14k that year.
2022–2023: Sharp inversion → crypto bear market under tight Fed policy → but expectations of rate cuts in 2024–2025 helped fuel recovery.
🔹Final Thoughts
A rising 2-Year yield and falling 30-Year yield is a red flag for the economy.
For crypto traders, the short-term impact is usually bearish as liquidity tightens.
However, this setup often marks the early stages of a cycle where, once the Fed is forced to cut, crypto benefits from renewed liquidity and investor risk appetite.
In other words:
📉 Short-term pain → 📈 long-term gain (if you can survive the volatility).