
If you’ve been exploring ways to earn passive income in crypto, staking is one of the smartest strategies to consider. By helping secure networks and process transactions, you can earn rewards simply by holding certain coins. But not all staking opportunities are equal each cryptocurrency has its own rules, risks, and potential returns. Let’s break down staking strategies for Bitcoin ($BTC), Ethereum ($ETH), Cardano (ADA), and Solana (SOL).
What Is Staking?
Staking is the process of locking up crypto to support a blockchain network. In return, participants earn rewards—usually in the same cryptocurrency. You can stake directly through wallets or via platforms that pool multiple users’ assets.
When staking, keep an eye on:
PY/Yield: The expected annual return.
Lock-up periods: How long your coins need to stay staked.
Network participation: Active networks often reward more.
Risk: Possibilities include slashing, inflation, or platform issues.
BTC Staking

Bitcoin doesn’t natively support staking since it uses Proof-of-Work. However, you can earn yield via:
Wrapped BTC (WBTC) on DeFi platforms
Centralized platforms like Binance, Nexo, or BlockFi
Average APY: 3–6%
Pros: Lower risk, most recognized crypto
Cons: Rewards are smaller, centralized platforms carry custodial risk
ETH Staking
After the Ethereum Merge, ETH now uses Proof-of-Stake. You can stake directly on the network or through platforms like Lido or Coinbase.
Minimum requirement: 32 ETH for solo staking (smaller amounts possible via pools)
Average APY: 4–6% solo, 3–5% pooled
Pros: Competitive rewards, strong network
Cons: Lock-up until full withdrawals are available, congestion may affect yield

ADA Staking
Cardano’s Ouroboros PoS makes staking accessible for everyone. You can delegate ADA to pools without locking it up.
Minimum requirement: None
Average APY: 4–6%
Pros: Easy to start, flexible, low risk
Cons: Rewards vary by pool performance, slightly lower than some altcoins

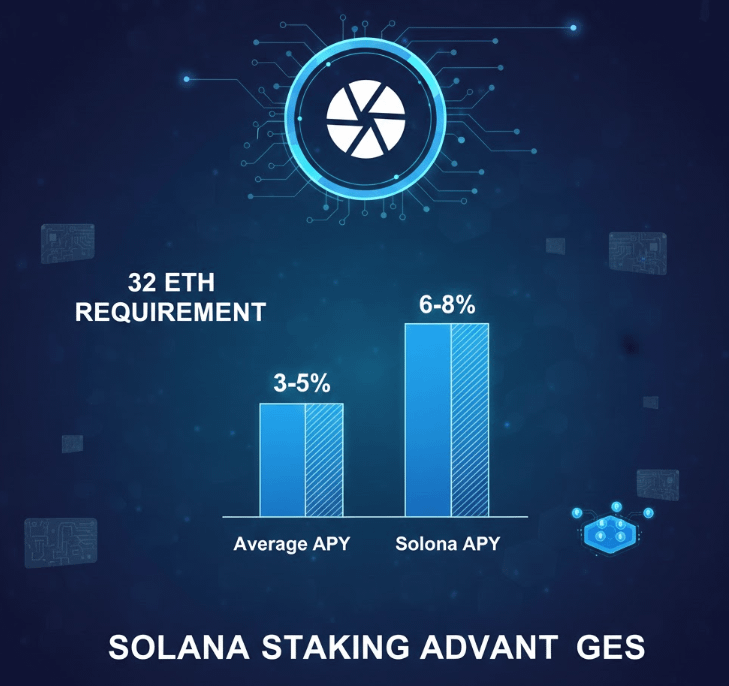
SOL Staking
Solana combines PoS with Proof-of-History, offering a fast and scalable network for staking.
Minimum requirement: None (delegation-based)
Average APY: 6–8%
Pros: High yields, fast network, growing ecosystem
Cons: Validator performance and past outages can affect rewards
Quick Comparison
BTC (Bitcoin)
Network Type: PoW via DeFi / centralized platforms
Average APY: 3–6%
Lock-up: Variable
Notes: Lower risk, but involves centralized platform exposure
ETH (Ethereum)
Network Type: PoS
Average APY: 4–6%
Lock-up: Until withdrawals are enabled (or validator exit queue)
Notes: Requires 32 ETH for solo validator, high demand network
ADA (Cardano)
Network Type: PoS
Average APY: 4–6%
Lock-up: None (delegation-based)
Notes: Easy delegation, relatively stable yield
SOL (Solana)
Network Type: PoS + PoH
Average APY: 6–8%
Lock-up: None (delegation-based)
Notes: Higher yield potential, dependent on validator and network performance
Tips for Maximizing Staking Rewards
Diversify: Don’t put all your crypto in one network; spread across BTC, ETH, ADA, and SOL.
Choose trusted platforms: Reliable validators and low fees matter.
Monitor networks: Keep an eye on outages, congestion, and updates.
Reinvest rewards: Compounding boosts your overall return.
Mix staking and DeFi: For BTC, lending or yield farming can increase earnings.