1. The Paradox of Digital Autonomy
The evolution of decentralized finance (DeFi) has created a significant strategic tension: while self-custody provides unparalleled digital autonomy, it simultaneously introduces a complex landscape of on-chain technical risks. Historically, wallet security was treated as a "set it and forget it" endeavor, focused almost exclusively on the physical or digital isolation of the seed phrase. However, in an era where professional users interact daily with diverse smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), this passive approach is insufficient. Security is no longer a static configuration but a dynamic, continuous process. Within the Binance Wallet ecosystem, security must adapt in real-time to the nuances of active on-chain participation.
There is a palpable industry shift as passive storage solutions, such as traditional cold wallets, evolve into active security management hubs. This transition acknowledges that holding assets is only half the battle; the other half is the ongoing management of the permissions and environments surrounding those assets. To bridge the gap between user autonomy and technical safety, modern architectures are integrating automated monitoring. By transforming the wallet from a mere container into a proactive defense mechanism, these platforms provide the necessary "architectural intelligence" to navigate the complexities of the modern blockchain landscape.
2. Deconstructing the Four Pillars of On-Chain Risk
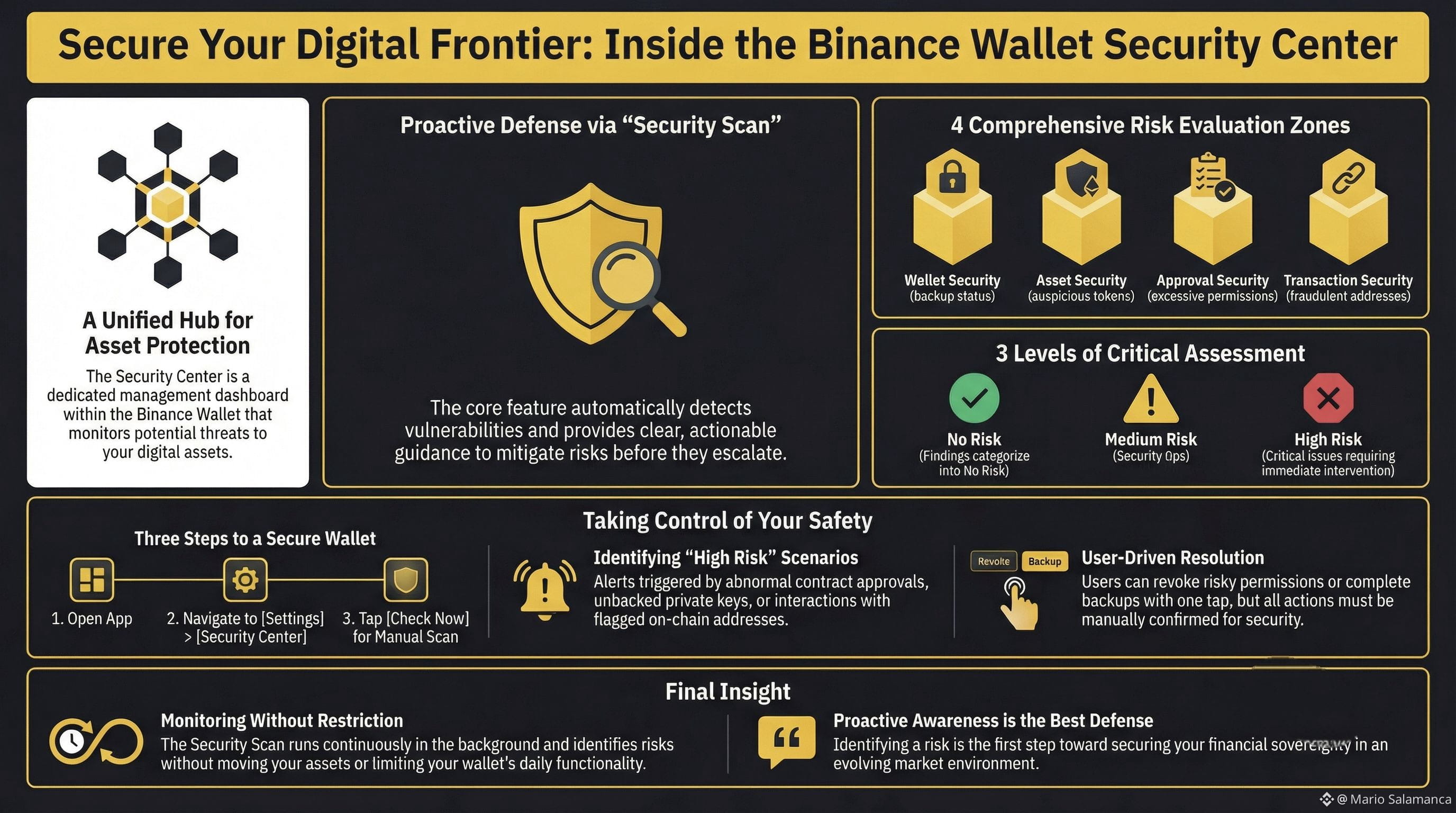
Protecting digital assets requires a multi-dimensional approach to risk assessment. Relying solely on seed phrase integrity ignores the sophisticated dangers inherent in smart contract interactions and peer-to-peer transfers. A comprehensive security strategy must evaluate the entire lifecycle of an interaction—from the local device environment to the finality of an on-chain transaction. In the Binance Wallet, this strategy is distilled into four critical security domains:
Environmental Integrity (Wallet Security): This pillar focuses on the operating environment and backup hygiene. By scanning backup status and the local device for vulnerabilities, the platform reduces the risk of unauthorized access or abnormal activity before a transaction is even initiated.
Asset Liquidity and Legitimacy (Asset Security): Not all tokens appearing in a wallet are benign. This domain reviews tokens and assets—including those on a user’s specific watchlist—to identify potentially high-risk or "poisoned" tokens. Proactive monitoring of the watchlist is essential to preventing interaction with malicious assets designed to exploit user curiosity.
Permission Management (Approval Security): Excessive smart contract permissions are the primary vector for "drainer" contracts in modern phishing attacks. This domain critically analyzes wallet approvals to detect high-risk or unnecessary permissions and provides the strategic capability to revoke them through a single, "one-tap" decisive action.
Counterparty Verification (Transaction Security): This pillar analyzes on-chain history and interaction patterns to prevent interactions with fraudulent or high-risk addresses. By acting as a final filter, it ensures that assets are not inadvertently sent to malicious actors.
These pillars function in concert to create a unified security interface, ensuring the user is protected across every layer of their digital asset management experience.
3. The Logic of Real-Time Risk Categorization
In the high-velocity DeFi environment, automated background scanning is a strategic necessity. By removing the requirement for manual audits, the Binance Wallet significantly lowers the "cognitive load" for the professional user, allowing them to focus on portfolio strategy rather than technical forensics. Risk detection is most effective when it is continuous, operating in the background to provide real-time notifications on the homepage without requiring manual initiation.
To provide clear intelligence, the platform maps risk into three distinct levels:
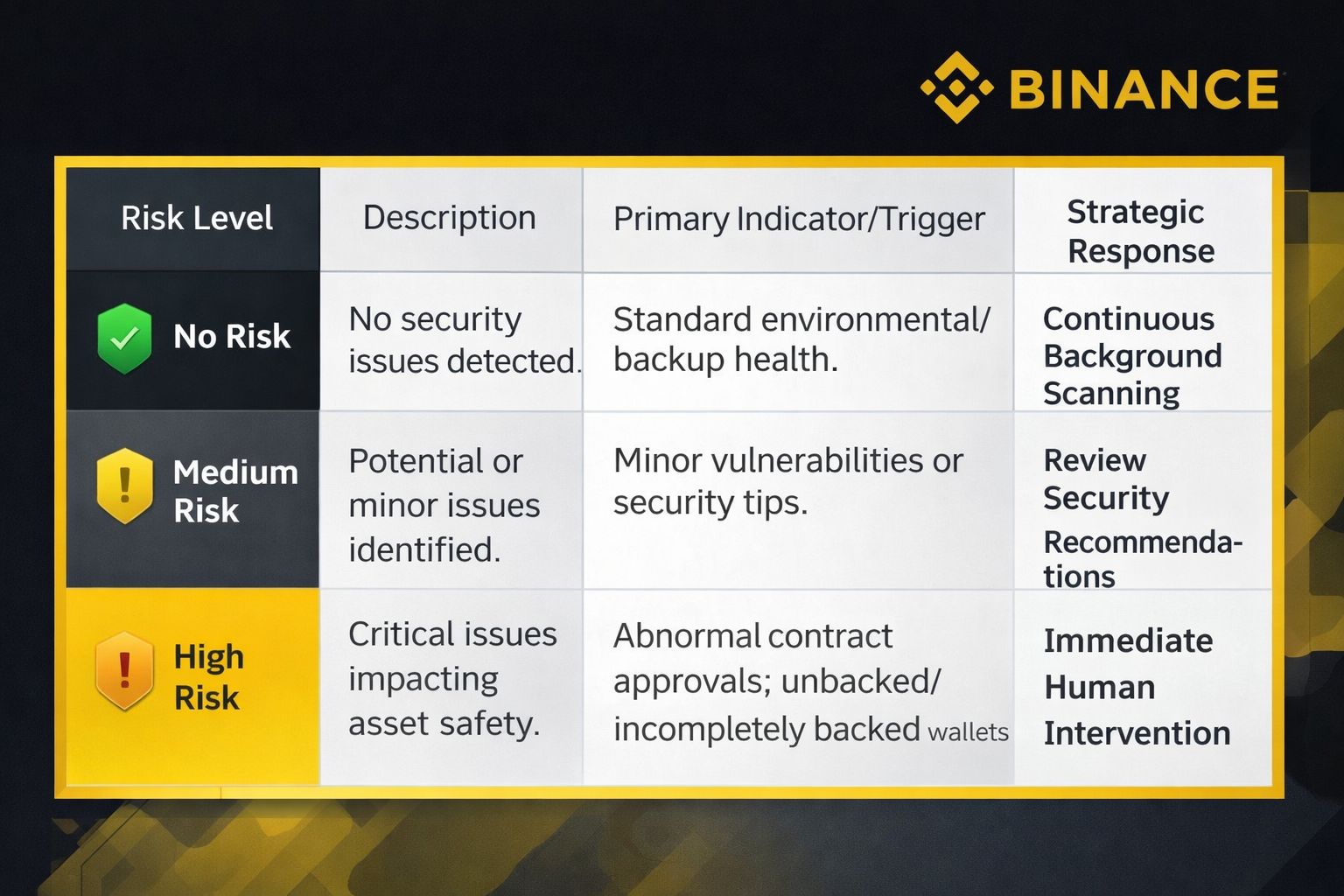
The system specifically triggers "High Risk" alerts for the weakest links in management: abnormal contract approvals, unbacked or incompletely backed wallets, and interactions with suspicious addresses. While the system automates detection, the final execution of security actions remains a human-in-the-loop responsibility. This is a critical safeguard against algorithmic overreach, ensuring that while the software identifies the threat, the user retains ultimate sovereign control.
4. Strategic Implications for the DeFi Ecosystem
The movement toward integrated security hubs has profound implications for diverse wallet architectures. By supporting both "Keyless" (Multi-Party Computation or MPC-based) wallets and traditional seed-phrase wallets within a single platform, the Binance Wallet centralizes risk management without compromising decentralization. For MPC-based architectures, where traditional recovery phrases are absent, a centralized security management layer is not just a luxury—it is the necessary infrastructure for institutional-grade safety.
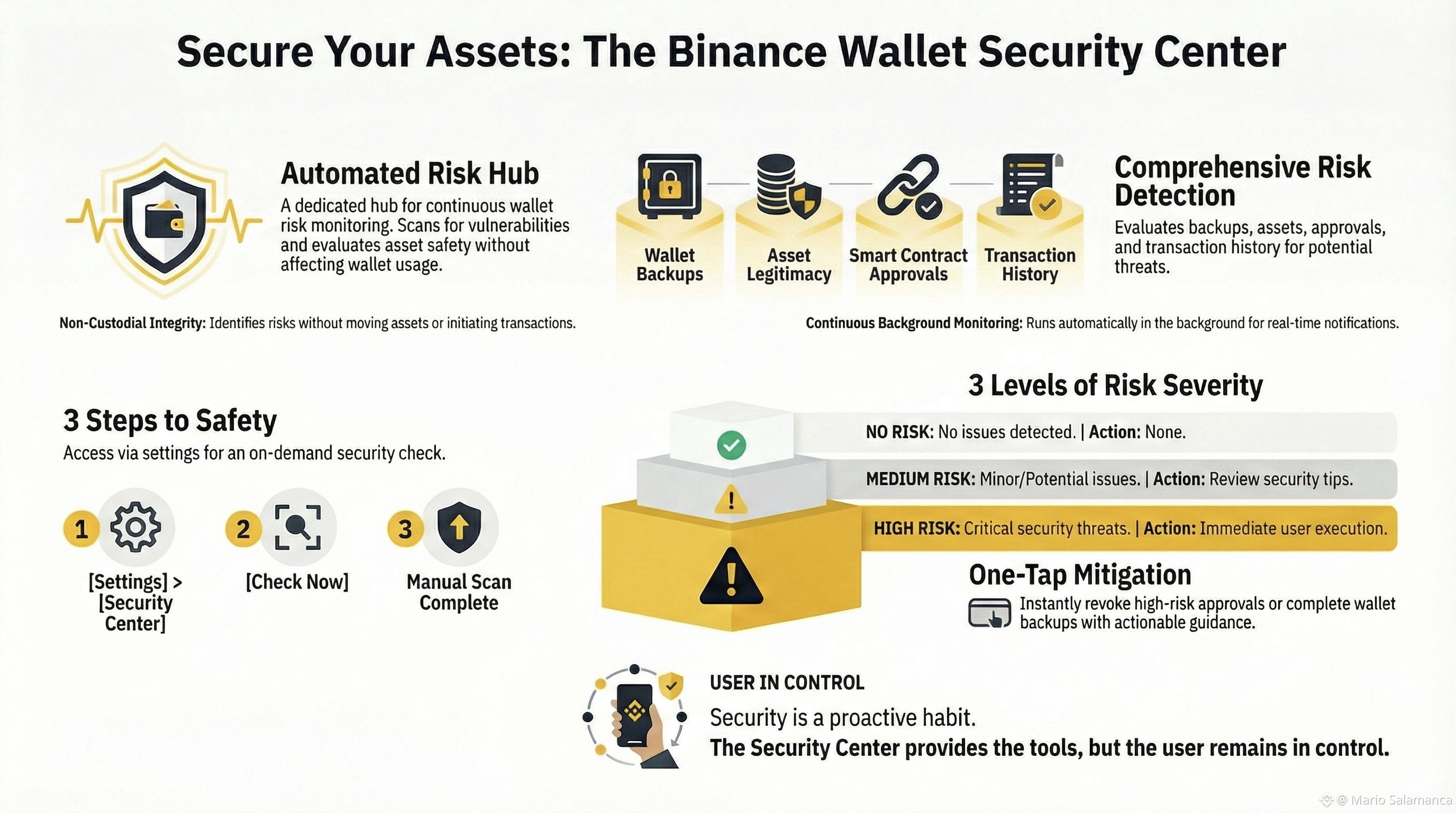
For the professional risk manager, the deployment of "Security Scans" offers three critical takeaways:
Preservation of Non-Custodial Integrity: These scans are purely informational. The Security Center acts as an informational layer that does not have "spend" permissions, ensuring the non-custodial nature of the wallet is strictly maintained.
Zero-Touch Scanning: Scans do not initiate transactions or move assets. They provide the user with the intelligence required to make informed decisions without interfering with the underlying liquidity.
Automated Vigilance: Continuous background monitoring ensures users are notified of threats—such as new malicious approvals or "poisoning" attempts—the moment they appear on-chain, rather than after a loss has occurred.
5. Closing Reflection: The Security Mandate in a Volatile Market
The integration of automated scanning, one-tap approval revocation, and environmental health checks marks a turning point in the evolution of self-custody. In the current market context, where institutional and retail interest in on-chain finance continues to expand, the complexity of the ecosystem has outpaced the ability of even sophisticated users to perform manual due diligence. Institutions, in particular, demand high levels of on-chain transparency and risk mitigation before committing significant capital to decentralized protocols.
The burden of security must therefore shift: it can no longer rest solely on the technical expertise of the individual, but must be embedded within the wallet’s architectural intelligence. This shift is the only way to safely scale DeFi to the next billion users. Moving from reactive disaster recovery to proactive risk mitigation is not merely a technical upgrade; it is a prerequisite for the long-term viability of the digital asset economy. Ultimately, the future of decentralized finance depends on the ability of platforms like the Binance Wallet to provide a secure environment where users can exercise their digital autonomy without the constant threat of exploitation. Proactive risk management is the foundation upon which the next era of global on-chain finance will be built.
