In the Dusk network architecture, Kademlia's Distributed Hash Tables (DHTs) are used to build efficient and structured peer-to-peer (P2P) networks. Specifically, they are integrated into the Kadcast protocol, which handles node discovery, routing, and message propagation. Compared to traditional gossip protocols, DHTs offer significantly improved performance.
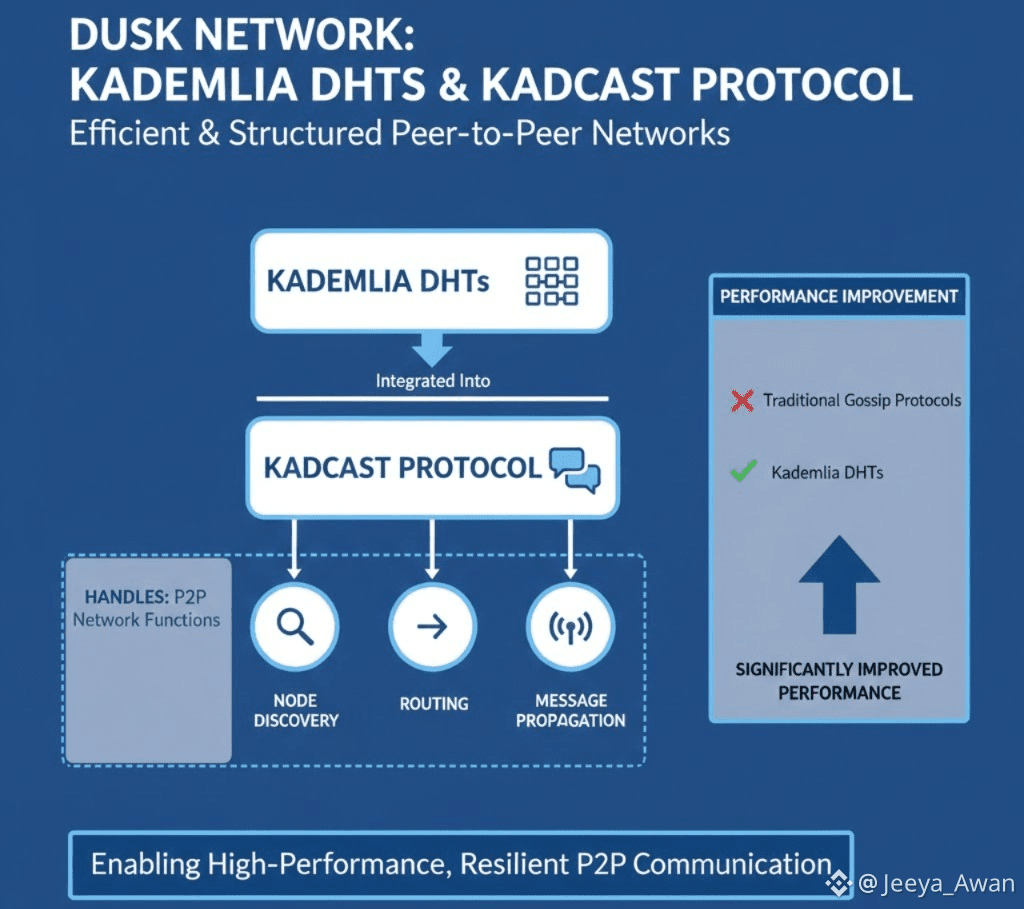
• The role of Kademlia's DHTs in the Dusk network architecture
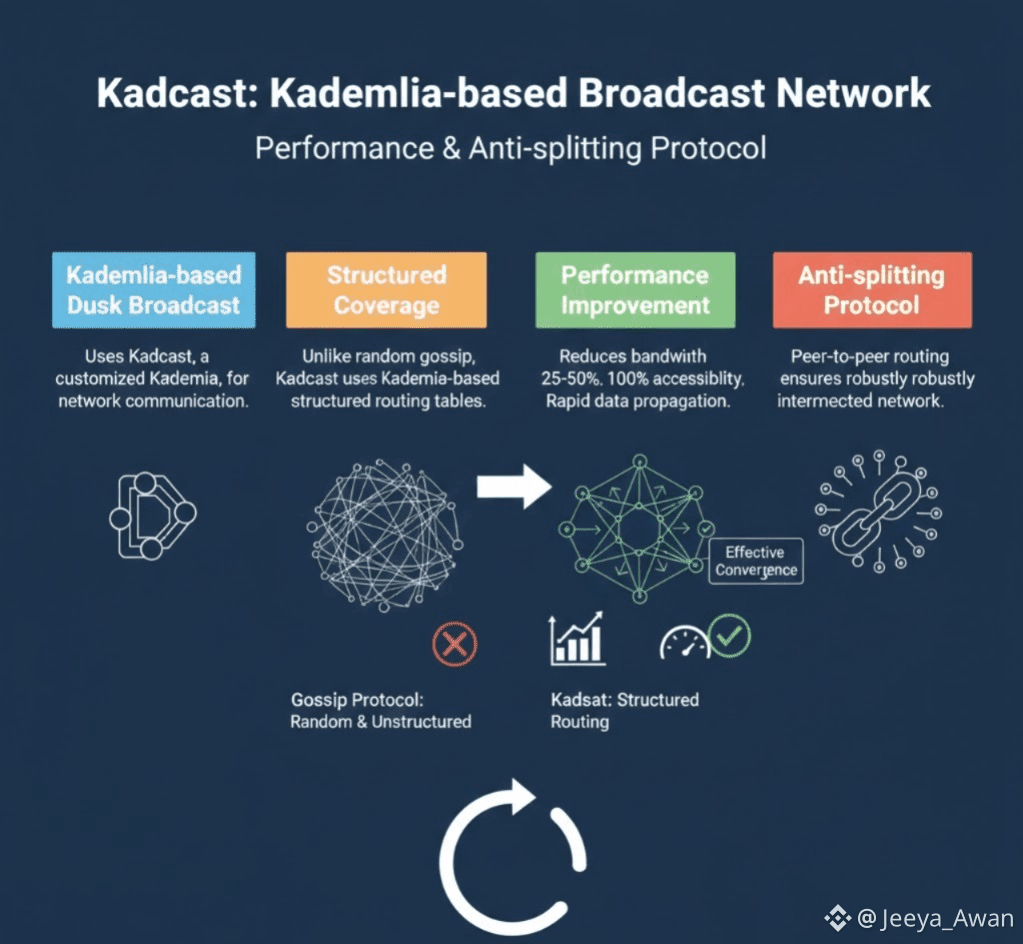
1. Kadcast: Kademlia-based Dusk broadcast networks use Kadcast, a customized version of Kademlia, for network communication.
✓ Structured Coverage: Unlike the random and unstructured gossip protocol that generates redundant messages, Kadcast uses Kademlia-based structured routing tables.
✓ Performance Improvement: This approach reduces bandwidth usage by 25% to 50% while maintaining 100% accessibility, thus facilitating the rapid data propagation required for effective convergence.
✓ Anti-splitting Protocol: Kadcast, as a peer-to-peer anti-splitting routing protocol, ensures the network remains robustly interconnected.
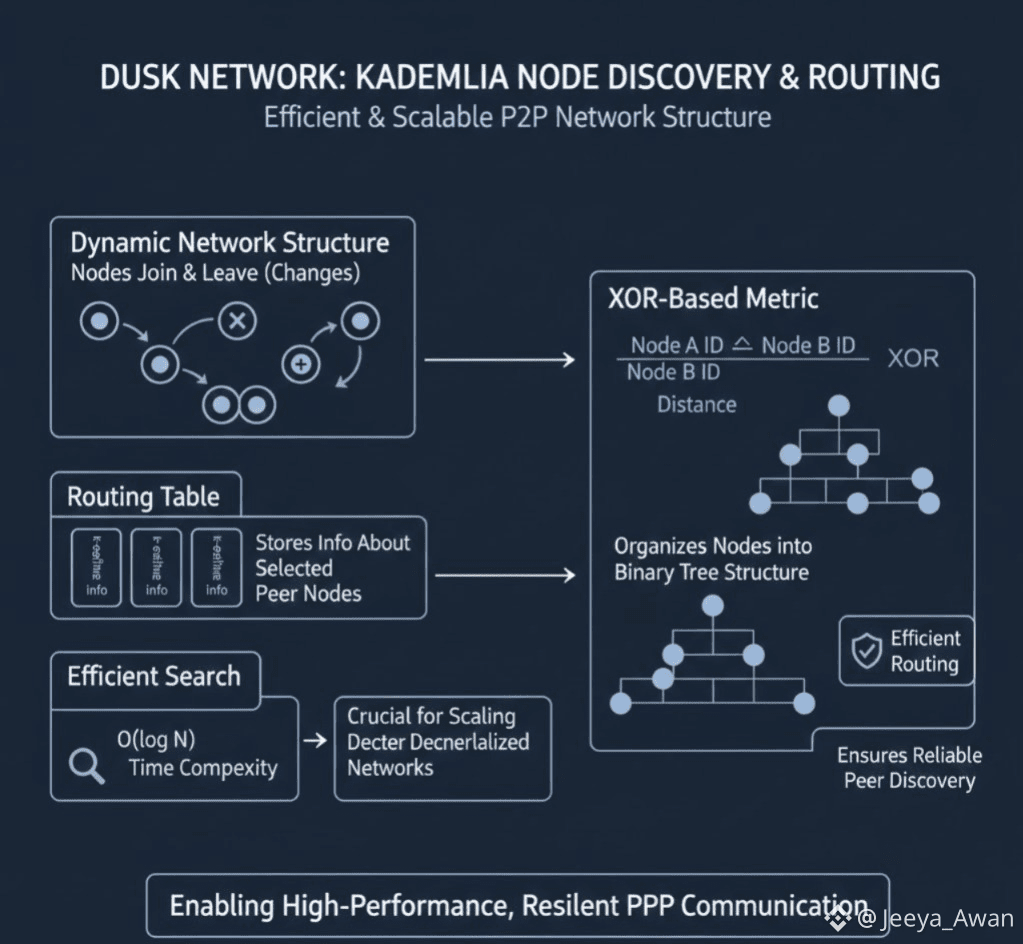
2. Node Discovery and Routing: Kademlia's core functionality maintains the network structure as nodes join and leave (changes). ✓ Routing Table: Nodes maintain k containers to store information about other carefully selected peer nodes.
✓ Efficient Search: The network supports O(log N) time complexity searches to locate peer nodes or resources, crucial for scaling decentralized networks.
✓ XOR-Based Metric: Kademlia uses an XOR distance metric to determine the distance between two node IDs and organizes them into a binary tree structure for efficient routing.
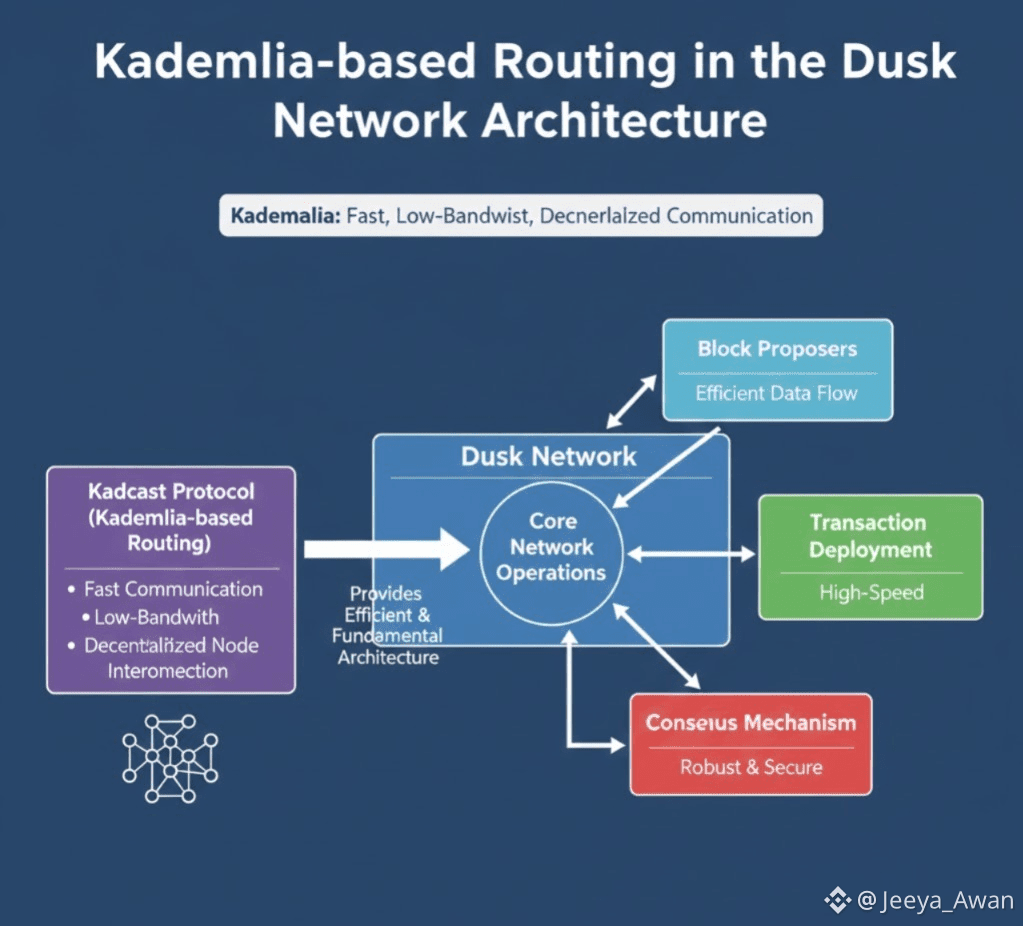
3. RASC Integration and Consensus Mechanism: The Kadcast protocol integrates into a broader RASC network architecture, which includes RASC virtual machines (for zero-knowledge private transactions) and a concise proof consensus mechanism.
✓ Efficient Deployment: DHT ensures transactions can be quickly deployed to block proposers.
✓ Separation: Kadcast enables the network to separate transaction deployment from the actual block negotiation phase, helping to maintain the average block time at approximately 10 seconds.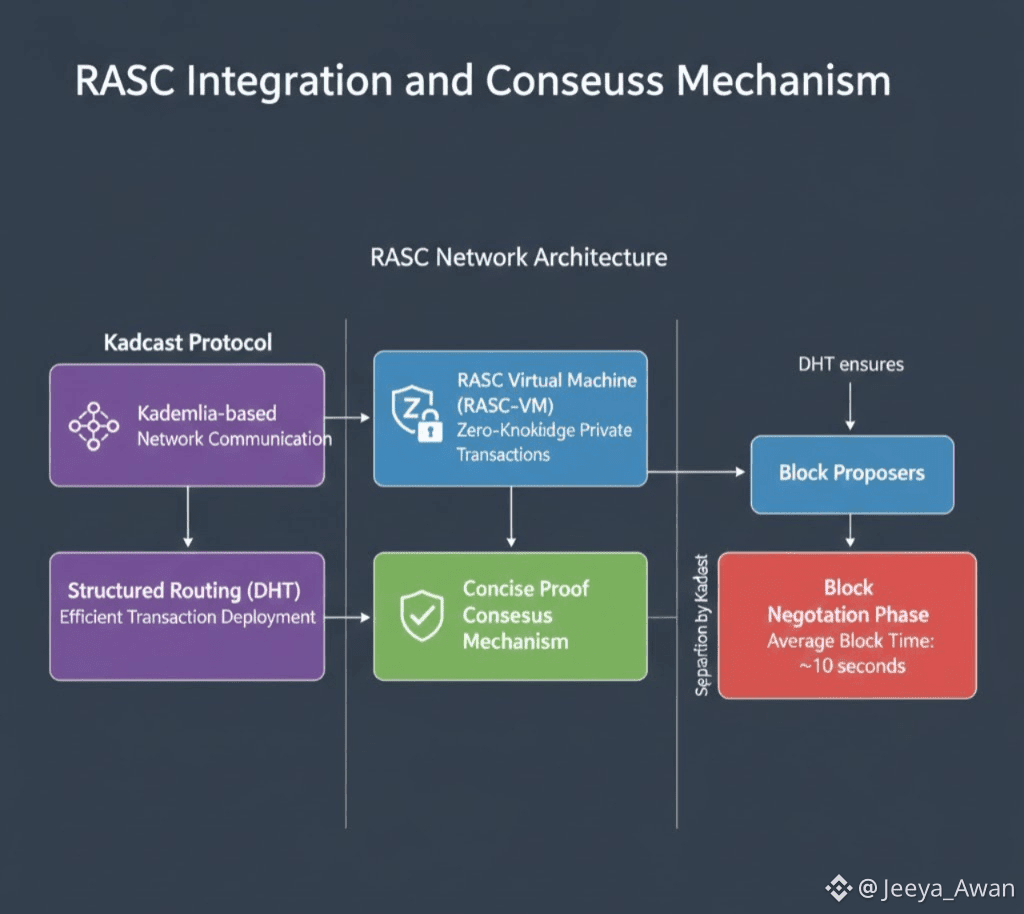
4. Scalability Advantages of the Dusk Network: DHT technology allows the network to handle a large number of nodes.
✓ Fault Tolerance: Due to the parallel and asynchronous nature of Kademlia queries, the network can handle node failures without significant performance degradation.
✓ Resistance to Sybil Attacks: By prioritizing long-running nodes (high-availability nodes), Kademlia enhances the network's resistance to certain types of attacks, such as Sybil attacks.
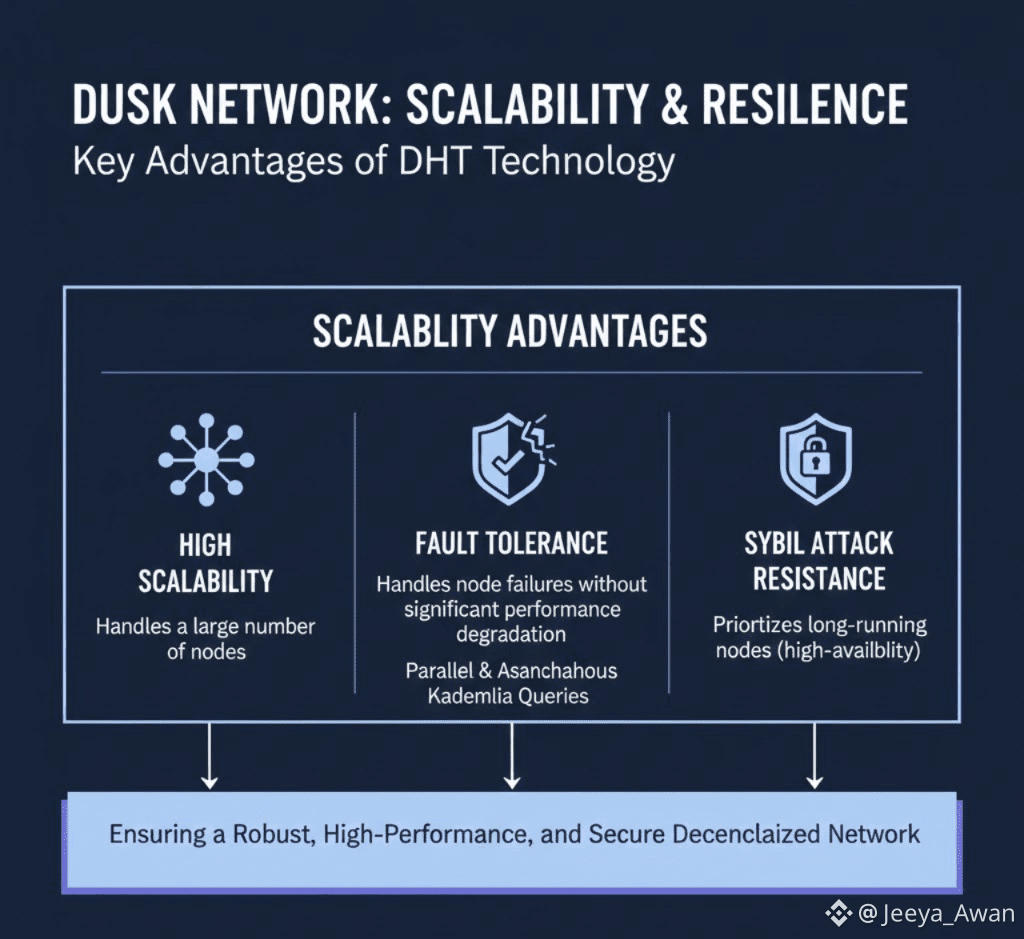
Kademlia (through Kadcast) provides an efficient and fundamental routing architecture for the Dusk network, enabling fast, low-bandwidth, and decentralized communication between nodes.