When people talk about AI on blockchain, they usually focus on launch conditions.
Can it deploy?
Can it execute?
Can it process transactions?
Those are the wrong questions.
The real stress test begins after success.
Because autonomy doesn’t fail at deployment.
It fails under sustained scale.
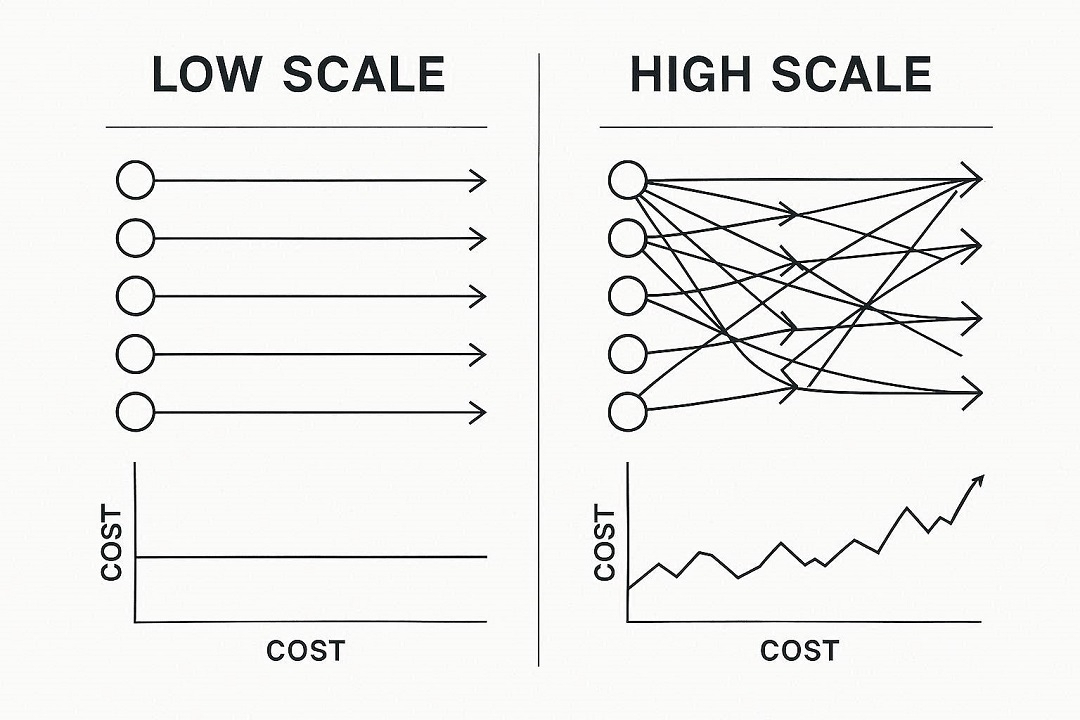
Scaling multiplies cost sensitivity
An AI system executing 100 transactions per day can tolerate volatility.
An AI system executing 10,000 per day cannot.
When execution frequency increases:
Fee variability compounds.
Budget forecasting becomes unstable.
Treasury management becomes reactive.
If infrastructure pricing fluctuates under demand, scaling does not increase efficiency.
It increases fragility.
Scale magnifies structural flaws.
Latency becomes systemic, not technical
At small scale, minor latency shifts are irrelevant.
At large scale, latency variance creates:
Asynchronous state inconsistencies.
Execution misalignment.
Increased retry loops.
Cascading computational overhead.
What looks like a minor delay becomes structural drift.
Autonomous systems require deterministic behavior patterns.
Not “usually stable” execution.
Congestion reveals hidden architecture
Many networks behave differently under stress.
Block ordering shifts.
Finality timing changes.
Gas estimation becomes less reliable.
At small scale, that is manageable.
At large scale, it creates model uncertainty.
AI systems are not tolerant of execution randomness.
They depend on consistent environmental conditions to maintain logical continuity.
Dependency amplification
The more autonomous the system becomes, the more dangerous external dependencies are.
Off-chain memory layers.
External computation services.
Third-party storage.
Each dependency adds:
Failure probability.
Latency variance.
Security surface area.
When scale increases, those risks multiply — not linearly, but exponentially.
What works at prototype level collapses under production load.
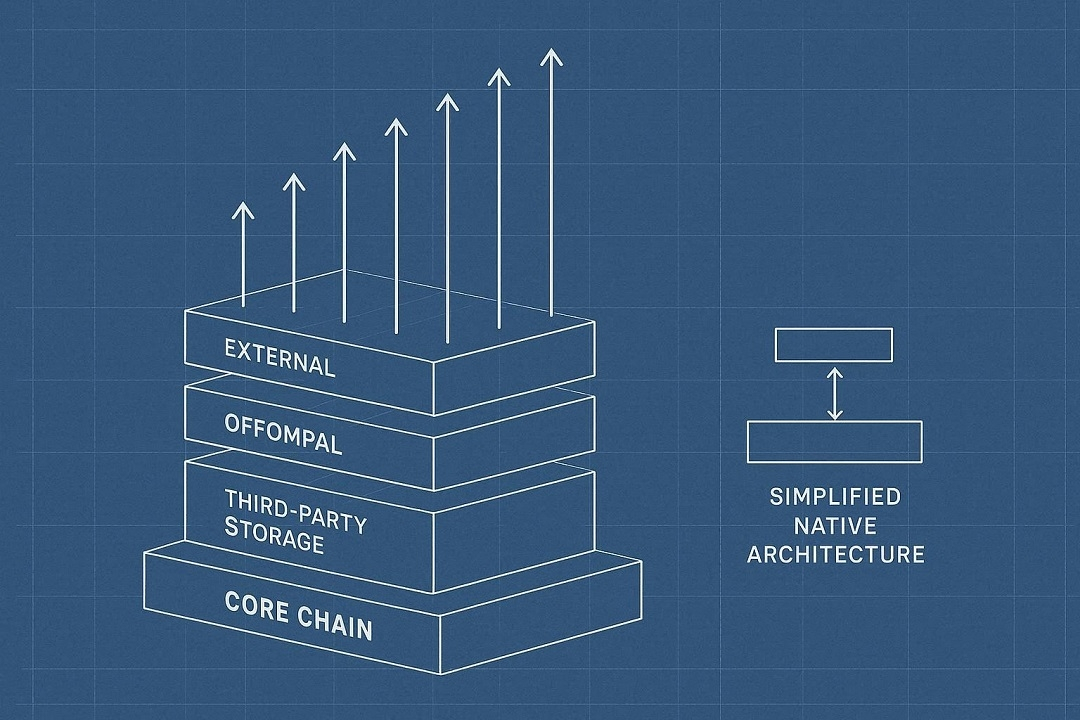
True autonomy is environmental control
Autonomy is often defined as “no human intervention.”
But that definition is incomplete.
True autonomy requires:
Predictable execution costs.
Stable ordering mechanics.
Deterministic performance under load.
Minimal external dependencies.
Without those, the system is not autonomous.
It is conditionally automated.
And conditional automation breaks under volatility.
Conclusion
Scaling is not a growth problem.
It is an architectural test.
Many AI-on-chain experiments succeed in controlled environments.
Very few survive environmental pressure.
The difference is not marketing.
It is structural design.
In environments where execution costs remain predictable, ordering mechanics do not shift under congestion, and AI infrastructure operates natively instead of relying on external layers, scale stops being a fragility multiplier.
It becomes an efficiency amplifier.
That architectural distinction is not cosmetic.
It determines whether autonomy survives real-world volatility.
